Category: The pack attack
Problems With Fred Davies #2: His Claims On Knives, Wounds And Stains Also Highly Mislead
Posted by James Raper

Several of the numerous scientific witnesses; some evidence was behind closed doors
Overview Of This Post
Remember that Amanda Knox, a felon for life, served three years for framing Patrick for murder.
In my previous post I dismissed the claim which the British barrister FG (Fred) Davies pervasively made in Parts 1 to 20 of his mammoth series in Criminal Law and Justice Weekly that it was actually Guede and his team who had somehow framed Knox and Sollecito for a crime he alone committed and left all of Italian law enforcement bamboozled.
I now have Parts 21 to 26 as well, all of the series, and I wish to examine one more large area of cherrypicked facts and misinterpretations, along with Davies’s final conclusion.
First, Fred Davies’s Final Scenario
As anticipated, Davies concludes that Knox and Sollecito should only have been convicted of the charge of simulating a burglary. He presents his own synopsis of what happened on the night of the murder which has both Knox and Guede present at the cottage for the murder, but not Sollecito.
Davies says it is Guede who sexually assaults and stabs Meredith. Knox, unaware of what was going to happen is horrified and scared out of her wits, retreating to her bedroom and locking herself in.
Davies says Guede flees, ignoring or unable to do anything about the fact there is/was a witness to his horrific crime. When it’s safe to do so Knox emerges and meets up with Sollecito.
Davies says that Knox, fearing that if she went to the police she would only end up being accused of involvement in the murder, persuades Sollecito to be her alibi, and to stage the scene to point to a burglar, and Sollecito, being the Honour Bound sort of chap he is, agrees to go along with this. Once they both embark on this course of action there us no turning back.
I trust that you are all duly intrigued with Davies’s scenario and panting to learn how and why he arrives at it. Unfortunately this will have to wait until another day if it is to be from me.
He has, after all, taken 26 Chapters in half a year to get to this point and I am not yet ready to deal with them comprehensively. Others here may contribute posts and discuss implications with the Criminal Law editor.
Fred Davies On Knife Or Knives
Whilst I guess most comments are going to be about the above synopsis, I am going to deal with his thoughts regarding the knives, these being quite central to his synopsis.
My argument below is supported by numerous previous posters none of whom differed markedly from Massei or Nencini.
Davies in contrast is sharply critical of Massei. He simply excludes the Double DNA knife (Exhibit 36) as the murder weapon.
He is also critical”¦.nay, I would have to say that he is outraged”¦. at Massei holding that Sollecito was responsible for the lesser of the two wounds, that on the right side of Meredith’s neck. He is critical of Micheli for not finding, as a matter of fact, that Guede was the one responsible for the wounds, using his own knife which has yet to be recovered.
Without more ado I will proceed to Mr Davies’ evaluation:
“The finding against Sollecito that it was he who inflicted two of the three wounds to Meredith Kercher using a pocket knife which was in his possession at the material time is deeply flawed, offensive and wrong in law”
Well, I was unaware that Massei had found that Sollecito inflicted two of the three wounds. In fact I am not aware of three wounds (unless he includes what is effectively a nick) , but if there were then Massei only attempted to attribute two, the one to the right of the neck, 4 cms deep and with a width of 1.5 cms, being attributed to Sollecito’s “pocket knife”.
It did not cause any significant structural damage, unlike the wound to the left, 8 cms deep and 8 cms wide which had penetrated both Meredith’s larynx and the cartilage of the epiglottis, and had broken the hyoid bone.
Is the rest “deeply flawed, offensive and wrong in law”?
“It could not have been part of the prosecution case that Sollecito used a pocket knife to subdue and stab Meredith Kercher. If it had why was Sollecito and/or Knox not charged with carrying the said pocket knife without justified reason? To recapitulate,, the charge alleged that the killing was achieved by means of”¦”¦”¦”¦.and deep lesions to the left anterior-lateral and right lateral regions of the neck, caused by a bladed weapon (Exhibit 36).
The Massei Court’s finding strikes against basic principles of fairness which applies to all criminal proceedings. Put another way, a criminal court is not generally entitled to bring in a verdict which differs markedly from the basis on which the prosecution puts it’s case. This is because the defence would not be able to adequately prepare and meet such an unexpected contingency. In plain English the defence would be ambushed or taken by surprise. In this case the defence was ambushed and the defendants’ rights (Knox and Sollecito) were fundamentally infringed.”
Oh come on! Ambushed? Really?
OK, so the charge did indeed indicate that that both the right and left sided wounds were caused by “a bladed weapon to which Chapter B applies” (Exhibit 36) but the reality is that the defence always knew that Exhibit 36 (because of it’s dimensions and in particular it’s width 4cms from the tip) could not have been the cause of the wound to the left anterior lateral. That’s a matter of simple logic and in any event every expert and all the lawyers in the case agreed on that.
So the way the charge was erroneously framed in fact misled no-one.
Indeed had the defence thought so then they could have raised the matter. Mr Davies does not claim that Massei did not have the power to amend the indictment. If the court was unable to, or the defence chose not to raise it, either way thinking it was a clever appeal point, then it did not become one.
Indeed, Mr Davies will know anyway that in English law, by virtue of The Indictments Act 1915, courts can (and frequently do) order an amendment to an indictment at any stage (which includes during a trial) provided the amendment does not result in an injustice to the accused. This is a practical necessity as it would be an affront to the concept of justice if defendants were to be acquitted on the basis of a mere technicality.
One might consider what amendment might have been made.
A possibility is that reference to the right-sided wound might have been excluded. It was the left-sided wound that was fatal, after all, and caused, as the prosecution would endeavour to prove, by a weapon which, as it happened, belonged to Sollecito.
The prosecution did, of course, maintain that it was Knox who wielded the weapon, but might, as an alternative, have also asserted that it was Sollecito. Indeed the framing of the charge leaves it an open question as to which of them did. They were charged jointly with having caused Meredith’s death.
The evidence that it may have been either (AK or RS) is a common feature of cases to which the English legal doctrine of joint criminal enterprise applies.
The doctrine applies particularly to a case such as this in that no matter who actually wields the weapon the other participant in the common enterprise is deemed to possess the same level of criminal liability even if he did not know that there was a knife or that it would be so used. Being reckless as to that possibility is sufficient.
It is surprising how often how little is required to establish joint enterprise. Frequently the mere fact that the participants know each other and were there, and that the situation was a combustible one of the group’s making, is enough. The doctrine has come in for a great deal of justified criticism but despite this remains firm law.
My preference would have been to amend the indictment to refer to the right sided wound being caused by a bladed weapon, the blade being of indeterminate length but with a width of approximately 1.5 cms. It is the width of the wound that is salient because it is indicative of the width of the blade on the knife being used which, whilst also being indicative of the likely length of the blade, but without being sure, could be either a pocket knife (4 cms or more) or a flick knife (which could also be a pocket knife). 1.5 cms is about the width of the tip of one’s index finger, by the way.
Massei, and others, always refer to this knife as a pocket knife. However henceforth I am going to write “pocket knife” to refer to the options of a pocket knife with a blade of 4cms or more, or a flick knife.
As to Mr Davies other point as to why Sollecito was not specifically charged with carrying a “pocket knife” without justified reason, I do not know, but since the framing of charges is a matter for the prosecution, one might as well leave the matter there.
In any event the lack of a specific charge does not in any way preclude a court from inferring the nature of a weapon from the pathology of the wound nor from identifying the probable assailant (as distinct from having to prove beyond a reasonable doubt the culpability of a single perpetrator named in a specific charge of “carrying”).
Guede did not ever face a specific charge of carrying a weapon but that does not prevent Mr Davis from concluding that Guede had a knife and had stabbed Meredith. It seems that Mr Davies would have been quite happy for Guede to have been so charged and convicted on Professor Vinci’s (see later) dubious testimony.
In this last respect, however, Mr Davies could have more telling argument. Lets see.
“To infer that Sollecito had a pocket knife at Via della Pergola 7 on the fateful evening of November 1-2, based on the character evidence of four witnesses called for the defence, was to say the least highly unusual..”
I think the operative words here are “witnesses called for the defence”, amongst whom was Sollecito’s own father. Yes, highly unusual but then that is what happens when you do not vet your own character witnesses before cross-examination.
Sollecito’s proclivity for carrying a knife (usually a pocket knife) at all times (and indeed he had one on him at the time of his arrest in the Police Station) is highly relevant. These witnesses referred to a knife with a blade of about 4 cms, or perhaps 6 cms.
In addition Sollecito was something of a knife aficionado. The police found two specialist knives, a Spiderco and a 2004 model Brian Tighe. Neither of these can be connected to Meredith’s wounds but they are indicative of his affinity to weapons specifically designed to be used in a fight to maim or kill. Clearly a flick knife falls into the same category.
As to proclivity evidence against Guede one can refer to his brief possession of a kitchen knife acquired at and belonging to the Milan nursery (which he did not break into, he had been given a key).
There is, of course, Tramontano’s dubious claim (angrily dismissed by Micheli even though Guede was never given the chance to challenge this in court) that a black man broke into his property and, confronted by Tramontano, had pulled out a flick knife as he exited. Tramontano tried to claim the burglar was probably Guede based on a photo of him he had seen in a newspaper. If it really was Guede he was not carrying that knife with him at the Milan nursery 8 weeks later.
“Even if Sollecito was present at the scene of the crime (as distinct from being complicit), the court could not have been sure that any “pocket knife” in his possession, which incidentally was never recovered, had inflicted all or some of the injuries, the most cogent rationale being:
1. The prosecution could not prove the dimensions and the character of the knife were consistent with the injuries inflicted upon Meredith Kercher.
2. The Court paid scant regard to the totality of expert opinion as to the type of bladed weapon (or weapons) which had been used to stab the victim
3. The Court paid scant regard to the dimensions of a bloody outline of a knife found on Meredith’s pillow
4. Consequently the Court could not have been sure that any pocket knife and, a fortiori, exhibit 36 had been used to stab Meredith that fateful night.”
As to 1 above, we know that no suitable weapon was ever recovered but if the indictment had been amended in accordance with my preference then the prosecution would easily have proved that part of the indictment, relating as it does to the wound on the right side of the neck.
It is a reasonable inference on the balance of probabilities that the wound was caused by a “pocket knife” and if one accepts the presence of multiple attackers (which I understand is a judicial truth in the case even following the latest acquittal of Knox and Sollecito) then, again on the balance of probabilities, and taking into account all the other circumstantial evidence in the case, I submit that it is a reasonable inference that it was Sollecito’s “pocket knife”.
The bar of “beyond a reasonable doubt” applies to culpability re the specified charge and is not to be confused with the elements.
As to 2, this simply is not true. I shall look at the totality of the expert opinion in a moment but suffice it to say that Massei spent a considerable amount of time in his Motivation detailing with and discussing the defence experts’ opinions.
As to 3, (and it was not on the pillow but the bedsheet) it was Professor Vinci’s contention that the bloody outline (there was a dual outline, he said) was left by a knife with a blade 11.3 cms long or a knife with a blade 9.6 cms long with a congruent section of handle 1.7 cms long (9.6 + 1.7 = 11.3). Davies does not mention a blade width but in fact Professor Vinci actually says 1.3 to 1.4 cms wide.
Taking these measurements as read, Davies points out that they are incompatible with either a pocket knife (such as Sollecito had a proclivity to carry) and Exhibit 36. I have no argument with that observation. It follows, he then argues, that one has to infer the presence of a third knife in any hypothesis and if a pocket knife and Exhibit 36 are already accounted for by Knox and Sollecito then a reasonable inference is that the third knife would have to be Guede’s. Indeed (Davies does not say this, but I will) Professor Vinci’s blade is not incompatible a priori with either of the two wounds.
This is worth looking at seriously as so far it is the only worthwhile point Davies has made.
First of all I have to say that I have searched for but have not found any rebuttal evidence or comment from the prosecution amongst the documents on the Wiki. I do not even see a question on the matter in the cross-examination of Professor Vinci.
Massei only briefly commented about the bloody outline on the bed sheet. He opined that the blood stains were certainly “suggestive” but insufficient to establish any clear outlines from which reliable measurements could be established. Clearly then he did not accord any reliability to Professor Vinci’s measurements. But is Massei right? One does not have to be an expert to consider this.
First of all, here are images of the blood stains.
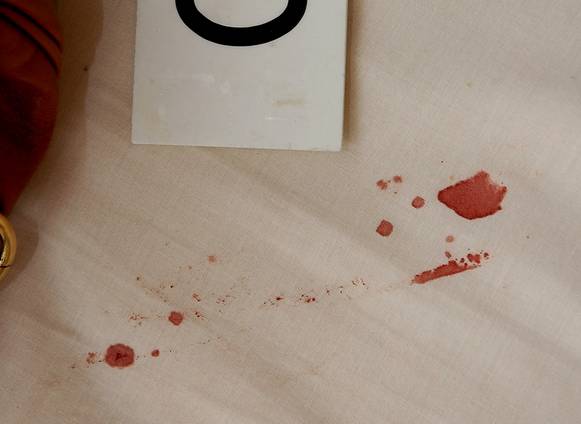

In the picture below the stained section of sheet is cut out for analysis the day after the discovery of the murder.
Did the prosecution overlook their own analysis of the stains? Did they deliberately do so after Exhibit 36 was found, 9 days later on the 12th November, to have Meredith’s DNA on it? Or did they always know that the stains established nothing?

The next question to be asked is whether we can see the outline of a knife, or rather a blade. I think the honest answer to that is, on balance, yes. We think we see the tip of a blade, do we not? Maybe two, maybe even three.
It is fairly clear that Professor Vinci takes the largest of the stains to be the hilt of the handle to the knife. Lining that up with what is perhaps the likely clearest possible perceived blade tip (being the middle out of a possible three I believe I see) then the distance to the perceived hilt is indeed something like the 9.6 cms which Professor Vinci has measured.
But there are problems. Here are two of Ergon’s photos from his posts here and here with Exhibit 36 superimposed on the stains in two different positions to reflect the supposed dual outlines.
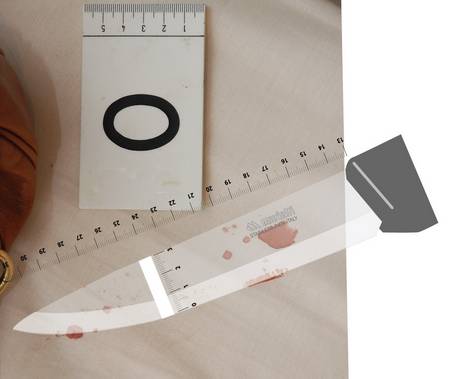

The blob of blood in the bottom left of the pictures and it’s lesser moon at 1, or 2, o’clock are regarded as having come from the same position on the blade and so with that reference point the blade is positioned accordingly in each photo.
We can surely take it that Professor Vinci also sees the same duality. But if the bloody hilt is aligned to fit with “the moon” stain in order to get the 9.6 cms measurement, then what has happened to that large hilt stain when the knife is moved further to the left, and then dropped a bit, to align to the moon’s planet (the blob)?
It has either disappeared or become an edge. That doesn’t make sense if “the moon” is the lesser version of the blob. The blob has to come from the first positioning of the knife. Despite this, in the knife’s later position the volume of blood at the hilt has actually increased comparative to the knife’s first position. That doesn’t make sense either.
So maybe the largest stain pre-exists, even for perhaps a moment, the stains suggesting the blade outlines, but in that case we can throw Professor Vinci’s measurements out of the window.
Can we do without the blob and it’s moon? It’s all a lot less convincing without them. But in truth we cannot even be sure that they are related. Nor that the largest stain has anything to do with the hilt of a knife.
A further connected observation concerns Professor Vinci’s claim that the blade of the knife is 1.3/1.4 cms wide. Like the rest of his evidence I do not find this very convincing. I suspect that he has deduced this from the largest stain which has a length, he says, of 1.7 cms. It’s width could then be something like 1.3/1.4 cms.
If the width of the knife is represented by approximately 1.4 cms then, given the position of the bloody hilt relative to the tip of it’s blade, what are we to make of the two spots of blood in a horizontal line above? They look like the upper (or lower) edge of a knife but they can’t be without making the blade wider.
Why does it have to be the same knife anyway? The stains could be the result of two different knives collected and laid to rest in the same spot.
The blood stains are certainly bewitching - rather like seeing patterns in tea leaves at the bottom of one’s cup - but on the balance of probabilities I would not totally rely on anyone’s perception of them even, with all due respect, Ergon’s but his analysis is as good as anyone’s, and that for me is the point of it.
In short I think that Massei was probably right. These stains are suggestive but basically useless and the police/prosecution ignored them for that reason.
“Consistent with English law the Massei Court’s findings should be struck down as Wednesbury unreasonable. Where there is no evidence to support a finding of a court or the court has reached a conclusion which is irrational or perverse, in the light of the evidence adduced at trial, a conviction based on that part of the evidence cannot be sustained”¦”¦”¦.The Massei Court also appears to have violated Article 6 of the European Convention on Human Rights (the right to a fair trial),”
Yeah, right. The case to which he refers, Associated Provincial Picture Houses v Wednesbury Corporation [1948] 1KB 223, is an odd and unnecessary one to pray in aid. It was a civil case where the appellant sought judicial review in respect of a licencing decision. As a formulation of a first principle of natural justice it is, of course, unquestionable. However the claim that Massei reached a conclusion that was irrational or perverse is laughable.
It is at this point that one does begin to wonder whether Davies is indeed connected in some way with the daffy Nigel Scott (Sollecito”˜s ex Lib Dem Haringey Councillor groupie) who similarly emerges with bizarre arguments.
Next, in his evaluation, we come to a numbers game as to who was for and against the incompatibility of Exhibit 36 with the fatal wound on the left side, but before I enter into that game I want to make a point about incompatibility.
A knife blade is only incompatible with a wound if the depth of the wound is longer than the length of the blade or if the width of the wound is shorter than the width of the blade at the relevant depth.
We can therefore establish that Exhibit 36 was not incompatible, a priori, with the depth of the wound. The blade on Exhibit 36 was 17. 5 cms long and the depth of the wound was 8 cms.
Yes, I know that other arguments as to incompatibility were advanced based, in the main, on these measurements. These Massei logically deconstructed. In fairness to Mr Davies he did not advance them in his evaluation and so neither shall I.
I would also have to concede that Sollecito’s “pocket knife” is not incompatible a priori with the wound on the left side nor, even if it”˜s length of blade was over 4 cms, with the wound on the right. Nor Professor Vinci’s knife either.
The same is true of the width of these knives.
It should however be recalled that the width of the right-sided wound was also 8 cms. That is over 5 times the width of the “pocket knife”. The width of the blade on Exhibit 36 - 8 cms from it’s tip - was twice the width of the blade on the “pocket knife”.
This fact, and the robustness of the larger weapon, particularly with regard to the observed butchering at the base of the right-sided cut, makes Exhibit 36 a far more likely candidate, in my submission, than a “pocket knife”, and that’s without taking into account Meredith’s DNA on the blade.
Returning to our numbers game, Mr Davies puts it slightly differently from Massei. He says -
“And if that were not enough, of the 8 experts who gave evidence on the point, two (Dr Liviero and Professor Bacci) opined that Exhibit 36 could have caused the fatal wound to Meredith’s left side. Professor Norelli could not rule out Exhibit 36. Professor Ronchi’s opinion is not clear due to the use of the “double negative” (non-incompatibility) - it will be assumed that he supported the prosecution contention, but in any event al the remaining four experts, Professors Introna, Torre, Cingolani and Dr Patumi) opined that Exhibit 36 could be ruled out.”
In other words a draw but one of the prosecution experts is a bit “iffy”.
Massei tells us that Dr Liviero concluded “definite compatibility”, Dr Lalli and Professors Bacci and Norelli “compatibility” whilst “non- incompatibility” came from the 3 GIP experts nominated at a preliminary hearing. The latter were Professors Aprile, Cingolani and Ronchi.
“Non-incompatibility” is not hard to understand. It simply means not incompatible or rather, compatible.
Note that Mr Davies has Professor Cingolani lining up to exclude Exhibit 36. Massei disagrees and I agree with Massei. So, for what it is worth (and this is a bit childish I know) Mr Davies loses the game 7 - 3.
“And one final thought. If the defendants (Knox and Sollecito) were sufficiently compos mentis to dispose of the pocket knife “¦. Why did they not dispose of Exhibit 36? By a process of deduction and logical synthesis the answer is plain for all to see: Exhibit 36 never left Corso Garibaldi and was not the murder weapon “
Because it was on his landlord’s inventory of kitchen items? Indeed we don’t know for sure that the “pocket knife “was actually disposed of. All we know is that it was not identified and recovered by the police.
And In Conclusion
This is the second of my posts involving Mr Davies. I may not be disposed to do any more. I have to say that although he certainly provided some food for thought on this one, I have not been impressed with his analysis in the topics I have covered so far.
Others here have been tabulating other factual errors and forced arguments and as I mentioned at the start we may see them carry this a bit further.
Problems With Fred Davies #1: Did Guede’s Separate Trial REALLY Impact Negatively On RS And AK?
Posted by James Raper
1. Summary Of The Complaints
I want to write about the separate trials of Guede on the one hand and Knox and Sollecito on the other.
This feature has often been criticized by the apologists for Knox and Sollecito, and I was surprised to learn just recently that their gripe seems to have some support in learned establishments in the UK! Ahem.
The gripe concerns the Fast Track trial of Rudy Guede, and the consequent Supreme Court confirmation of his conviction, with the apologists arguing that these had an adverse and unfair effect upon the proceedings in which Knox and Sollecito were involved. It is based on the simple fact that Guede chose to be tried separately, this being seen as an unfair complication for the administration of justice in the Italian justice system.
There are a number of complaints that the usual apologists have regarding the separate trial of Guede. Most of these are in fact fantasies as I will address.
These complaints, or constant refrains, which some apologists fondly thought could form the basis of a complaint to the European Court of Human Rights in due course, can be summarised as follows -
1. That the proceedings concerning Guede established various tenets the most important one of which was the multiple attacker scenario, and that this unfairly affected Knox and Sollecito bearing in mind that their defence was based on the Lone-Wolf scenario.
2. That the evidence in the Guede proceedings could never be effectively challenged by the Knox and Sollecito camps.
3. That, in consequence of which, Knox and Sollecito had virtually already been convicted by the judiciary by the time of their own trial.
4. That Guede was allowed to give evidence against Knox and Sollecito at both his own trial and at the Hellmann appeal hearing without effective cross-examination. Had this been the case the defence would likely have exposed and demonstrated his sole responsibility for the murder of Meredith Kercher. Indeed had he been tried together with Knox and Sollecito this could well have happened at the Massei trial.
5. That Hellmann was right to give no probity value to the content of Guede’s sentencing and the subsequent annulment unfairly allowed material that was prejudicial for the aforesaid reasons into the Nencini Appeal.
6. That Guede was induced into electing for a separate trial with the promise of a reduced sentence should he be convicted - this being to prosecution’s advantage re the case against Knox and Sollecito.
2. How Overall The Complaints Are Wrong
I think that we know what fast-track is by now, so I will not dwell on that. Guede’s trial was over relatively quickly. It lasted a month and likely consisted of about 3-4 hearings. There were just a few witnesses called.
The judge, Micheli, in addition, dwelt on all the evidence in the investigative file including witness statements and forensics. This was because Guede was charged with murder “in complicity with others” and because Micheli also had to make the decision whether or not to commit Knox and Sollecito to stand trial as the other accomplices.
Before I address whether or not there could be any justification at all for the apologists’ above complaints I would like to mention that learned quarter to which I referred at the outset.
I recently stumbled (with the help of the apologists’ website) across the Criminal Law and Justice Weekly website.
I was surprised to learn that various articles had been appearing on it under the heading of “The Brutal Killing of Meredith Kercher - A critical examination of the trials and subsequent appeal hearings of Rudy Hermann Guede, Amanda Marie Knox and Raffaele Sollecito.”
Lexis Nexis ( publishers and distributors of legal material to the legal profession in the UK) describe Criminal Law and Justice as”¦.”the leading weekly resource for criminal law practitioners and all those working within the courts and criminal justice areas.”
The articles are by an F. G Davies, described as a Barrister and listed in Anthony and Berryman’s Magistrates Court Guide as a Deputy Justices Clerk, North Cambridgeshire, in England. He is also a contributor and specialist editor to Justices of the Peace Law Reports.

Online image associated with an annual legal-fees guide which FG Davies edits
Here are two quotes I picked out relevant to this post about separate trials.
“This supports the writer’s contention made earlier that the holding of separate trials for co-accused was wrong in principle and law because the prosecution were alleging that at all three defendants committed the crime acting in concert”
And:
“It provided Guede with a golden opportunity to minimize his part in the attack upon and murder of Meredith Kercher, loading the blame on to Knox and Sollecito who, by this time were suspected to be chief architects of the attack.”
It is of course perfectly true that in the anglo-saxon world Guede would not have had the choice to elect for trial separately from his co-accused. It might have made for a very interesting trial for everyone concerned if he had stood trial together with Knox and Sollecito, but for reasons I will explain later I doubt it, or that Knox and Sollecito would have gained any advantage from it.
Indeed separate trials had rendered a very specific advantage to the Knox and Sollecito camps in that Guede had already been convicted when Knox and Sollecito stood trial, a fact that their PR campaign and followers have drilled home at every conceivable opportunity.
But what on earth does it mean to say that “the holding of a separate trial [for Guede] was wrong in principle and law”? .
Whose law? Whose principles? Just how deeply does the Deputy Justices Clerk delve into the respective systems of justice (and particularly the Italian one) for a comparative evaluation?
Certainly on the basis of a quick read of his articles I would say that he hasn’t delved very far at all. In fact I will go further and say that despite that he is capable of a detailed review of various aspects of the case he pretty much shares the same hostility and concerns based upon parochialism and ignorance to be found on the usual apologists’ websites.
So I will try to put him and the apologists right on how the Italians cope, as a matter of law, with any evidential difficulties that separate trials can throw up.
However, let’s start first with the assertion that the fast-track trial “provided Guede with a golden opportunity to minimize his part in the attack upon and murder of Meredith Kercher, loading the blame on to Knox and Sollecito”? Is that true?
Guede admitted that he was present at the scene of the murder and he has always minimized his part in the attack, in fact denying that he had any part. This is all to be found in his statements pre trial. He would have minimized his part even if he had been tried with his co-accused and had given evidence. Given that he was not believed anyway, it is difficult to detect wherein lies the golden opportunity of a fast track trial.
It is also difficult to envisage what cross examination formula (and the point of it) would have been available to the Knox and Sollecito defence teams as to Guede’s minimal role or otherwise given that Knox and Sollecito maintain that they were not there and thus are hardly in a position to dispute Guede”˜s version.
Did Guede load the blame onto Knox and Sollecito? The answer to that is that he did directly implicate Knox but not Sollecito. Again this is all to be found in his pre-trial statements and interviews with the police and investigating magistrates. Whilst on the toilet he had heard the doorbell ring, Meredith call out “Who is it?” and later say “We need to talk” followed by another woman’s voice, which he thought was Amanda, replying “What’s happening?” He had also claimed to have seen, through Filomena’s bedroom window, a female figure with flowing hair and had recognised the shape as being that of Amanda Knox.
It might be useful at this point just to pause and remember when Guede could have been cross-examined on this by the Knox and Sollecito defence teams.
Guede was called to give evidence during the Massei trial but declined to give evidence. Not surprising given that he was appealing his own conviction at the time. This was heard two weeks after the conclusion of the Massei trial.
He then appeared at the Hellmann trial by which time he already had a definitive conviction. On this occasion he did respond to questioning and I shall look at this a little later.
3. The Specific Mistakes In Each Complaint
Let us return now to the apologists standard refrains as I listed them at the beginning.
1. That the proceedings concerning Guede established various tenets the most important one of which was the multiple attacker scenario, and that this unfairly affected Knox and Sollecito bearing in mind that their defence was based on the Lone-Wolf scenario.
One might also add the staged break in and some others as well which were all considered by Micheli and endorsed by Massei.
However as at the conclusion of the Massei trial Guede’s first appeal was still extant and the Supreme Court’s definitive reflections on the multiple attacker scenario were still a year off. Nothing had been written in stone at that point. If the multiple attacker scenario became a tenet of the case then it would be more accurate to say that it became so because of Massei joining up with Micheli.
But let’s also take in the second refrain to consider alongside the first at this point.
2. That the evidence in the Guede proceedings could never be effectively challenged by the Knox and Sollecito camps.
This really is pretty rich. So what? Knox and Sollecito were not on trial there. And what to make of the Massei trial which of course is when Knox and Sollecito then wheeled out their big guns; the expensive lawyers and experts in telecommunications, forensic pathology, forensic DNA, ballistics and footprint analysis?
The Massei trial may have taken its time but it was nevertheless (unlike Guede’s trial) a full blooded adversarial trial of first instance, lasting a year, with the prosecution producing each and every one of it’s witnesses for rigorous cross-examination by the defence.
It was Massei that confirmed the multiple attacker scenario on the basis solely of that evidence and with scarce a mention of Guede’s sentencing report. It is lame to argue that Massei was in any way constrained by Micheli’s reasoning on the matter though his judgement was indeed available.
However Massei did make the following observation -
“”¦”¦the reconstruction of the facts leads to the unavoidable conclusion that he (Guede) was one of the main protagonists (writer’s note: no concession to Guede’s chances on appeal, then?); thus it is not possible to avoid speaking of Guede in relation to the hypothesised criminal facts. The defence of the accused in particular have requested the examination of texts concerning only Rudy, and have demanded the results, specifically concerning Guede of the investigative activities carried out by the police in particular. In fact they have expressly indicated Guede as being the author, and the sole author, of the criminal acts perpetrated on the person of Meredith Kercher.”
So here we see the defence making the running on Guede (without Guede being present as a co-accused to dispute anything) to include any and all evidence as to his alleged criminal background with the precise purpose of bolstering the Lone Wolf scenario, all of which was duly evaluated by Massei.
[One might think, in addition to the above, that Guede would have had cause to complain about the indictments for Knox and Sollecito, in that both were indicted, and subsequently convicted, with the crime of murder “in complicity with Rudy Hermann Guede”, although he still had two appeals left and theoretically (though not realistically) it was still possible for him to be acquitted of the crime. However the drawing up of indictments in separate trials, and how the judiciary would deal with an outcome such as above (which I don’t think would be difficult) would be a topic for another discussion.]
3. That, in consequence of which, Knox and Sollecito had virtually already been convicted by the judiciary by the time of their own trial.
This is so lame by any objective standard, but it is amazing just how often this particular drum is beaten. However our Deputy Justices Clerk would probably subscribe to this. He develops an argument akin to this which he terms the Forbidden Reasoning (echoes of Preston’s “The Forbidden Killer”?) which is basically that Micheli made a number of errors which were then compounded in subsequent hearings.
4. That Guede was allowed to give evidence against Knox and Sollecito at both his own trial and at the Hellmann appeal hearing without effective cross-examination. Had this been the case the defence would likely have exposed and demonstrated his sole responsibility for the murder of Meredith Kercher. Indeed had he been tried together with Knox and Sollecito this could well have happened at the Massei trial.
The evidence that implicated Knox I have already mentioned. It is not entirely decisive in that it is not a solid ID of Knox at the crime scene. At the Hellmann appeal Guede added this in an exchange with Knox”˜s lawyer -
DEFENSE ATTORNEY DALLA VEDOVA””And therefore, Mr. Guede, when you wrote verbatim that it was a “horrible murder of Meredith a lovely wonderful young woman, by Raffaele Sollecito and Amanda Knox” what do you mean exactly? Have you ever said this?
WITNESS””Well, I”¦ this, I’ve never said it explicitly, in this way, but I’ve always thought it.
DEFENSE ATTORNEY DALLA VEDOVA””And so, it’s not true.
WITNESS””No, it’s very true”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦.............. So if I wrote those words it’s because I’ve always had them inside of me. It’s not up to me to decide who it was who killed Meredith, in the statement that I made in my trial, I always said who was there in that home that damned night, so, I think I’m not saying anything new”¦”¦
In another exchange, this time with Bongiorno, Guede makes it clear that he is not planning to answer any further questions about what happened that night but this is because he has already stated (statements and recorded interviews etc), and stands by, all that he has to say about it. Thus all that is taken into evidence perfectly properly. The matter is then left to rest by the defence.
Indeed it is difficult to conceive what further effective cross-examination could have occurred in this situation because clearly Guede would have responded with exactly the same answer each time.
The above exchanges also show just why it is unlikely that there would have been any fireworks had Guede been tried with his co-accused.
Guede would not have been obliged to give oral testimony any more than were Knox and Sollecito and in the event that he had done so (and I think it would have been in his interests to do so) his evidence would not only have been the same but it would have been subject to the same limitations, which would have been zealously protected by his lawyers, that had protected Knox when she gave oral evidence.
On due consideration it might have been a somewhat tetchy affair for the lawyers but it would not have been in the interests of any of the respective teams of lawyers for there to have been any surprises such as Guede moving from beyond what he had already said in pre-trial statements to a solid ID of Knox from the witness box. That wouldn’t have particularly helped Guede as it would have affected his credibility even further. They all had prepared positions to protect and Guede’s presence would be neither that much of an added threat nor an advantage for Knox and Sollecito.
5. That Hellmann was right to give no probity value to the content of Guede’s sentencing and the subsequent annulment unfairly allowed material that was prejudicial for the aforesaid reasons into the Nencini Appeal.
Now we are into the law, Italian law that is, and how it coped with separate trials of co-accused.
By this time Guede’s conviction, remember, had been ruled as definitive by the Supreme Court.
This is what Hellmann said about that -
“”¦”¦. in truth, this judgement, acquired pursuant to article 238 and so utilisable under the probative framework only as one of it’s evaluative elements pursuant to article 192.”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦.. already appears in itself a particularly weak element, from the moment that this judgement related to Rudy Guede had been carried out under the fast track procedure.”
It will be useful to consider some of Prosecutor-General Galati’s observations in the prosecution’s appeal submission and we can do this because the Supreme Court agreed with him.
This is what the Supreme Court said -
“The submission on the violation of article 238 “¦”¦.is correct. Even though (Hellmann) obtained the final judgement pronounced by this court against Rudy Guede, after properly considering that the judgement was not binding, it has completely “snubbed” the content of the same, also neutralizing it’s undeniable value as circumstantial evidence on the presupposition that it’s profile was particularly weak, since the judgement was based at the state of proceedings without the enrichment acquired as a result of the renewal of the investigations hearing arranged on appeal, In reality, the court was not authorised at all, for this reason alone, to ignore the content of the definitive judgement.”
The enrichment referred to would of course have been the Independent Expert’s evidence (subsequently debunked by Nencini) and the Supreme Court also added that in any event article 238 was not impaired at all by the fact that the first instance trial was fast track.
At the end of the day this was just poor argument by Hellmann but it was symptomatic of the many flaws that underlay much if not all of his reasoning for acquittal.
More importantly for me and in addition to the foregoing the Supreme Court delivered a withering criticism of Hellmann’s understanding of circumstantial evidence and how to evaluate and treat it in its broad spectrum.
However, how can and what elements contained in the separate trial of one co-accused have any probative weight in the trial of the others?
Prosecutor-General Galati puts it like this. The Supreme Court’s rulings -
“have now settled definitively regarding the interpretation according to which finalised judgements can be acquired by the proceedings, as provided for by the indicated law, but they do not constitute full proof of the facts ascertained by them, but necessitate corroborations not differing from the declarations of the co-accused in the same proceedings or in a connected proceeding”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦”¦......
Naturally this confirmation is not directly used for the purpose of proof but as corroboration of other circumstantial pieces of evidence or of evidence already acquired, not very different from what happens when declarations of collaborators with justice corroborate each other.”
In the event the only material from Guede that really seems to me to have hitherto been extraneous to the first instance trial of Knox and Sollecito was the inclusion at the Nencini appeal of Guede’s partial ID of Knox at the scene and his evidence as to Meredith’s missing money, which were corroborative of elements of evidence that had appeared at the Massei trial; in the case of the missing money for instance, the missing credit cards and Filomena’s testimony that at a meeting shortly before both the murder and the day the rent was due Meredith had told her that she had the cash to hand and was prepared to hand it over there and then.
No such money was found at the crime scene. One suspects that these two elements would have been more prominent at the Massei trial, and have been motivated more attentively, had the three been tried together. In the event Guede’s partial ID of Knox was not even mentioned by Massei and Knox and Sollecito, in the absence of any evaluation of Guede’s evidence, were acquitted (not even motivated at all in fact) of the charge of theft in relation to the money and the credit cards.
Given the foregoing I would argue that Knox and Sollecito derived an advantage rather than a disadvantage from the separate trials.
Furthermore I would argue that the material from Guede’s separate proceedings was not particularly damaging given the overall context of the evidence already directly available from the trial of Knox and Sollecito (which received some but in truth did not require much corroborative confirmation from Guede’s separate trial) and which in itself was sufficient to found a verdict of “beyond reasonable doubt”, but it did supply some useful insight into a motive when of course Hellmann had found none and Massei had supplied a rather improbable one.
6. That Guede was induced into electing for a separate trial with the promise of a reduced sentence should he be convicted - this being to prosecution’s advantage re the case against Knox and Sollecito.
Needless to say this is what you get from desperate and deluded minds. Guede’s lawyer has explained why his client took his advice and the decision was perfectly rational and in Guede’s interests. Guede was entitled to a third off his sentence from choosing fast track though I am no fan of that. Furthermore I have explained why no particular advantage accrued to the prosecution from this choice other than that it probably foreshortened the time that a full trial of the three would have taken.
The Sollecito Trial For “Honor Bound” #5: Gumbel Just A Defamatory Anti-Italy Shill?
Posted by Our Main Posters

Above: “Neutral ghostwriter” Andrew Gumbel tweets…
1, Today In The Florence Court
Lately many of the chest-thumping PR shills have whined a lot more about themselves as victims than done anything to boost Sollecito and Knox.
Think of Preston, Burleigh, Dempsey, Sforza, Fisher, Moore, and a whole lot of other serial complainers. Now chest-thumper Andrew Gumbel seems to want to join their ranks. That is if the claim that he was ONLY a ghostwriter was made by his lawyer with his consent to the Florence judge.
2. Signs Gumbel Really Is A Shill
Note that Sollecito gave many signs during his US book promotion tour late in 2012 that he really didn’t know much about what was in his own book.
So did Gumbel really only hang on Sollecito’s every word? Or did he talk to a lot more people than that, and get very invested in nasty, dishonest propaganda to deny justice for Meredith via the courts?
Here’s Andrew Gumbel on 1 May 2014, providing the first media opinion in the UK on Judge Nencini’s appeal report. The nasty false claims highlighted suggest Gumbel has a very strong investment in Sollecito and Knox and not a little contempt for the Italian courts.
One truth in Gumbel’s article which he must really regret? That sentence in the thitrd paragraph: “Disclosure: I am the co-author with Sollecito on his memoir about the case.”
The longer the Italian courts consider the Meredith Kercher case ““ and we have now had three trials, six presiding judges, two hearings before the Italian high court and a third on the way ““ the more the country’s institutions of justice have covered themselves in shame.
Judge after judge has twisted the available evidence into extraordinary contortions of logic to assert, at different times, that Kercher ““ a British exchange student stabbed to death in her room in Perugia in 2007 ““ was the victim of a premeditated attack; that her murder happened spontaneously; that the motive was sexual; that the motive was a dispute over housework with Amanda Knox, the star defendant; that the trigger for the murder was the unseemly appetite Knox and her boyfriend, Raffaele Sollecito, had for sex and drugs; that the trigger for the murder was Rudy Guede, the Ivorian-born drifter everyone agrees was involved, knocking on the door to use the toilet.
By now, Knox and Sollecito have been convicted, acquitted and convicted again, and the underlying forensic evidence has been both exposed as a sham and, mystifyingly, reinstated. (Disclosure: I am the co-author, with Sollecito, on his memoir about the case.)
Still, the latest judicial document in the ongoing battle, a 337-page justification of the most recent convictions made public on Tuesday, marks a new low. Not only has Alessandro Nencini, the presiding judge of the Florence appeals court, apparently resorted to the same tortured logic as his predecessors; he has also stated things as fact that are manifestly and provably wrong.
That may be more than even the Italian justice system can stomach; judges, after all, aren’t supposed to do things like that. And it may provide Knox and Sollecito with unexpected ““ if still slim ““ grounds for hope at the very moment when Kercher’s death had seemed settled, at last, according to the law.
To read the new conviction report in detail is to enter a kind of alternate reality, where concrete facts appear ignored and alternate facts are seemingly plucked from the air. Kercher’s murder is reduced to a parlor game and all roads lead to the inevitable, if not also foregone, conclusion that Knox and Sollecito are guilty. For instance:
- On page 63, Judge Nencini claims that a partial shoeprint found at the murder scene comes from a size 37 women’s shoe and must therefore belong to Amanda Knox. But this is not based on the available evidence. In the early days of the case, the prosecution sought to show that the shoeprint was from Sollecito’s Nikes; the pattern of concentric circles on the sole was later proven to come from a different pair of Nikes belonging to Guede.
- On page 81, Nencini grapples with the question of how Knox and Sollecito could have participated in the murder but left no more than a single, hotly disputed trace of themselves at the scene. Extraordinarily, Nencini argues that Knox and Sollecito must have wiped the place clean of their DNA (but left an abundance of Guede’s) because no traces of Knox’s DNA were found anywhere in the apartment that she shared with the victim. But multiple samples of Knox’s DNA were found and presented at trial; they just weren’t found in the room where the murder took place.
- Then, on page 321, Nencini writes that the blade of the purported murder weapon ““ a large kitchen knife found in Sollecito’s apartment ““ bore traces of both Kercher’s and Sollecito’s DNA. Again, this is at variance with the evidence. The most the prosecution ever asserted was that Kercher’s DNA was on the tip of the blade. Sollecito’s DNA has never been found.
The defense teams have reacted with consternation: Knox issued a formal statement decrying the lack of “credible evidence or logic” in this latest document, which arrived just ahead of the three-month deadline following her latest conviction; Sollecito’s lead lawyer, Giulia Bongiorno, denounced what she said were “at least ten clamorous mistakes per page”. (A Kercher family lawyer called the document “a version that we have always in some ways sustained”.)
This being Italy, however, the judicial errors are not necessarily a bad thing for Knox and Sollecito, because they give the Italian high court an opening ““ should the justices choose to take it ““ to overturn the latest conviction, and either dismiss the case, send it back to get the mistakes fixed, or order yet another trial in another court.
The high court justices will be aware, of course, that the longer the case drags on, the more suspect the process will look in the eyes of world opinion. Another trial would test the patience of even the most ardent believers in Knox and Sollecito’s guilt, and certainly of the Kercher family. But the process is starting to curdle ““ even without the spectacle of lawyers arguing, yet again, over the same controversies before a barrage of international TV cameras. That leaves the high court, which always has one eye on the integrity of the system, with a genuine dilemma.
Much has been written about Italian justice’s desire to save face in this much written-about case. To admit a miscarriage of justice, the argument runs, has become too difficult, because it would expose the mistakes of too many people, from the primary investigators to the Rome forensic lab to the prosecutors and judges.
However, as the case trudges toward the seven-year mark, one has to wonder how much appetite the institutions of justice still have to stand by what they have done. Will the high court really want to endorse Nencini’s report with all these evident flaws? Or will this finally be the moment when the justice system calls a halt to a travesty committed in its name and exonerates Knox and Sollecito, as it should have done years ago?
3. How Gumbel Got It Wrong
We responded by rebutting 20 of Gumbel’s malicious claims in just the first 7 pages of Honor Bound. And Pataz1, a TJMK main poster who also runs his own blog posted this rebuttal of Gumbel below
This letter was sent to the Guardian’s Reader Editor on 4 May 2014, and again on 3 June, 2014. The Reader’s Editor did not respond to either of the email submissions.
Gumbel’s May 1st, 2014 article in the Guardian is a thinly veiled advocacy piece for Sollecito and Knox. He left out a significant phrase from a Nencini passage he cites; this phrase he omitted undermines one of his main claims.
To the Guardian:
I’m writing to you about Andrew Gumbel’s “comment” on developments in the murder of Meredith Kercher case. Gumbel writes about the recently released Nencini court motivations document, which outlines the court’s reasoning for affirming Knox and Sollecito’s conviction for the murder of Meredith Kercher.Gumbel waits until the end of the third paragraph in his article to provide his disclaimer: that he is a co-author of the book by one of the defendants. Its hard to understand why Gumbel waited so long to disclose his vested financial interest in the innocence of one of the defendants on trial. By this time, Gumbel has already levied allegations of impropriety upon the Italian courts and judges. For example, he alleges “the country’s institutions of justice have covered themselves in shame.” He continues specific allegations that “judge after judge has twisted the available evidence [”¦]”. If Gumbel had provided his disclaimer appropriately at the beginning of his letter, readers would have had a more appropriate understanding of Gumbel’s perspective and motivations for writing his letter.
Despite being a co-author of a book by one of the two still on trial for Meredith’s murder, Gumbel’s statements on the court process are wrong. Gumbel pushes the perspective that Knox’s reps have pushed in the US; that Knox and Sollecito have been “convicted again” after an acquittal. Gumbel leaves out any mention of the Italian Supreme Court ruling that overturned Knox and Sollecito’s acquittal and sent the case back to the appellate level. After the acquittal was annulled, the original 2009 conviction remained in place. Gumbel is no doubt aware that the Florence court is an appellate court. (Curiously, Sollecito’s co-defendant Knox also wrongly claims on her website that the Italian Supreme Court “annulled all previous verdicts”; ref: http://www.amandaknox.com/about-contact/?).
Gumbel’s omission of the Italian Supreme Court ruling is odd, because the entire point of his article is the integrity of the judicial decisions. Gumbel left out that the Italian Supreme Court has already made one ruling regarding the integrity of a judicial decision in this case. The Supreme Court’s ruling wasn’t in favor of Gumbel’s co-author and defendant Raffaele Sollecito; perhaps this is the reason that Gumbel failed to mention the actual outcome of the acquittal.
Or perhaps Gumbel left out this information so he could present the evidence the way it is framed by supporters of Knox and Sollecito. Later in the the same paragraph, Gumbel expresses confusion about why evidence remains in the case. He states “the underlying forensic evidence has been both exposed as a sham and, mystifyingly, reinstated.” As the co-author of the book with Sollecito, Gumbel is again no doubt aware that after the appellate-level acquittal was thrown out, the original conviction (with all of the evidence) remained as a part of the case. Any decision made by Hellmann on the evidence was also thrown out of the case, including Hellmann’s conclusions on the knife DNA evidence and the Sollecito’s DNA on the bra clasp. Further, if Gumbel had indeed read the Nencini decision, he would have read the passage where Nencini takes to task the “independent experts” in the Hellmann trial (detailed here:http://thefreelancedesk.com/amanda-knox-trials-meredith-kercher-case/). Gumbel should be well aware after his reading of Nencini why the evidence still contributed to the Florence court upholding his co-author’s conviction.
In his second point on the Nencini decision, Gumbel leaves out a key phrase that completely undermines his claim. By this time in his article, one is forced to wonder if this omission is deliberate. Gumbel’s claim is that Nencini contradicted himself by writing that Knox and Sollecito only left a “single, hotly disputed trace of themselves” despite the other evidence that Nencini also talks about. But the start of the passage Gumbel cites is:
“Una peculiarità è, ad esempio, il rilievo che all’interno della villetta di via della Pergola quasi non sono state rinvenute tracce di Amanda Marie Knox ““ se non quelle di cui si dirà e riferibili all’omicidio ““ né di Raffaele Sollecito.”
The phrase Gumbel deliberately left out is this: “se non quelle di cui si dirà e riferibili all’omicidio”, which, roughly translated, is “except those which will be discussed and related to the murder.” The Nencini Motivations document explicitly contains a clause that accommodates the other traces related to the murder. Gumbel’s point is provably false. As someone who arguably puts himself forth as an expert on the case, this omission is highly concerning.
In Gumbel’s third point he highlights what is a minor error in the Nencini report. Calling out one word in a longer passage, Gumbel points out the report states that Sollecito’s DNA was found on the knife that is alleged as a murder weapon. If Gumbel truly read the report, as he claimed in a twitter exchange with me, he would be aware that the rest of the section that is contained in makes it clear that the finding is Knox’s DNA on the knife, not Sollecito’s. This minor error is hardly cause to overturn the full conviction.
I could continue, but the rest of Gumbel’s article is largely a diatribe against the length of the trial and the Italian justice system. Gumbel cites an article written by Douglas Preston, another author who has financially benefited by being openly critical of the prosecutor in Knox’s case. Knox and Sollecito’s case has gone through three levels of the Italian court system, and back to appeals. Cases in the US that follow a similar path have not happened any faster than the one in Italy. For example, in the Scott Peterson case in the US his defense still filed appeals eight years after his first-level conviction.
That the Guardian has allowed itself to be used as a platform to push the defense’s perspective is not only a disservice to the family of the murder victim who lives in the UK, but is also a disservice to the victim of a violent, brutal murder.

