Political & economic headsup: US is demonstrating unsorted systems problems in spades. Do watch your investments. As Washington DC policy gets more & more off-target, big New York investors are betting very heavily that stocks will soon crash. Gross systems mismanagement 2017-20 tanked stocks several times.
Category: Cassation 2013
Monday, January 21, 2013
An Overview From Italy #2: Current Perceptions In Italy, Justice Perverters Fail, Mignini Vindicated
Posted by Machiavelli

My previous report on the bad news remorselessly building here for the defense was on the Procura Generale appeal to the Supreme Court.
One year ago ““ between the end of December 2011 and beginning of January 2012 ““ there were only rare idle comments in the Italian press about the Meredith Kercher case, more or less sarcastically noting the “suspicious” circumstances of the Appeal trial. I recall how a mention of the topic was dropped into the last number of “ll Venerdì” of 2011.
“Il Venerdì di Repubblica” is the weekly magazine issued together with the newspaper “La Repubblica” (thus probably the most read magazine in Italy).
The cover theme of that week was provincialism ““ or better “the provincials” - the adjective used to assemble a sample of seven little cities (Cuneo, Voghera, Rimini, Jesi, Perugia, Benevento, Partinico), picked from different regions, and taken as examples on the theme, that is stories of “local colour”; what goes on in small “provincial places”. A few characters and stories are brought in to depict the local life of each place, and the voices of local authors adds something about the places.
The article about Perugia (at pages 62-68) was by Luca Cardinalini. In that number of Il Venerdì, having stories of “local colour” as weekly theme, there were shades of ironic tones for each city, often through the voice of local intellectuals. As Perugia is described, the Meredith trial is quickly recalled among its local stories; the reader can’t miss how this is viewed as in connection with another most remarkable feature of the city, that is Masonry.
According to Luca Cardinalini and Enrico Vaime, Masonry is called a “Specialty” of Perugia, like chocolate. Local author Enrico Vaime intends to convey the people’s perception about shady powers existing in the city, about a local environment saturated by plots and informal powers, as something behind recent strange judicial decisions such as the Hellmann verdict and the apparent dropping of the Narducci case. The widespread belief of Perugians that the Public Minister (prosecutor) is the righteous one shines through the words of Enrico Vaime.
Also notice how racism appears to be another key perception about the verdict. Quality media press in Italy has a typical style of understatement. This comment hints that it seems obvious that the Appeal was a racist verdict - and it was “expected” that they would find a way to blame the black one and the outcast.
Some of Perugian “provincialism” seems to include a very narrow localism of Perugian identity: a person from Orvieto is reported to be called “a foreigner” ; but this is because the cultural viewpoint is based on the assumption of a personal knowledge of all people. In among this, there is Vaime’s knowledge about how rooted Masonic tradition and power is in the city, in a scenario of “brotherhoods” and “tribes” (the article includes a photo of the most known “Masonic” monument in Perugia: the gryphon or griffen ““ the emblem of Perugia ““ grabbing a toppled Pope’s Tiara in a sign of rebellion).
The report by Vaime is objectively correct : the concentration of members of Masonic lodges in Perugia is the highest in the world, about 5 times the national average of Italy (which is anyway very high).
In Vaime’s wording decent people in Perugia are ‘Christians’ or ‘Communists’ ““ these are the names he uses to address the main categories he sees as “good” people, two transparent moral systems. He devolves skepticism toward the less transparent allegiances, the murky and informal connections to powers.
I believe these perceptions from one year ago, in this colorful article about Perugia, should be most interesting to the readers of this site.
The first part of the article on Perugia is not that interesting - it speaks mostly about a local character named Ivano Massetti, nicknamed “Savonarola of Umbrian football”, the director (“boss”) of a local TV network and leading showman of his own soccer talk show. I skipped this first part with depictions of local folks, and get to the point at p.66 where the Kercher case is first mentioned.
This is my translation of the article from this point:
[”¦](p.66 line 17):
As Enrico Vaime ““ a 100% Perugian, a writer, and among many other things fiercly provincial ““ already knows: “Only in Perugia do you hear people saying “actually Tizio [random guy] was not a native from Colombella, but from Piccione”, which is three times further”. And when his grandfathers (farther of his father) bearing the same name Enrico Vaime, moved his formal place of residence [to Perugia] from Spello, on the official documents they wrote “emigrated to Perugia and married to a foreigner from Orvieto”.
The roots are extremely deep. “Still today” Vaime says “when I say to my family “we go back home”, I mean here, in Perugia, where I have not owned a house for decades. And I still call the roads and shops with the names they had when I was a child, even if now the owners are foreigners, from Shangai or, as I say, from Terni”.
Vaime is cross with the bad reporters who described Perugia, in the Meredith murder case, as a capital of corruption and vice: “An invasion of charlatan journalists who, as they believed they were visiting a remote and lost province, they painted it as a sort of Chicago on the Trasimeno Lake”.
[The fact] that no Perugian was involved in that sad story, to them that was an irrelevant detail. And the trial ended just the way many Perugians expected: a black guy first wrongly put in jail, another black one convicted, the two white, good-looking, wealthy and well defended young people, free.
So it was that the Public Minister Giuliano Mignini became a target. He’s a Perugian whom the Perugians know as the dominus of the other judicial case ““ this also is, yes, entirely local ““ about which everybody talks and knows, but always in a low voice: the death of doctor Francesco Narducci, the one suspected of having ties to the crimes of the Monster of Florence. From the judicial point of view that was - by half ““ just another hole-in-the-water [a failure] for which some critics have hastily put the blame on some alleged lunacy of the public minister.
But”¦ however”¦ meanwhile, this [Naducci] corpse-swap was indeed found to have been for sure, a kind of unique case in the criminal history of the country. And, for what concerns the recent acquittals of those characters involved in this death, well, after almost a year and a half we are still waiting for the verdict motivations. All of the suspects were esteemed high-class professionals. That’s a perfect mix of strange deaths, sex, lead-astray investigations, and Masonry; this is in the city with the highest number of Masonic lodges in Italy.
Vaime sighs: “Masonry is something alien from me, but I have many friends who are in it. In Perugia it works as a compensation chamber for various powers, but also as an effort for the surge of the spirit to many decent people. Masters, masons and “33”, but all of them decent Perugians”. Masonry is considered a local specialty, just like the bruschetta or the Etruscan arch.
“One day you find out that that mediocre employee of your acquaintance, or the one who performed an incredible career in the public administration or in politics, is a “˜son of Horus’. Then you either laugh, or you slap yourself on the forehead just like saying to yourself “Wow! [how could I ] think about it!”. “That travet* [*a generic mediocre opportunist employee], too”
Vaime says “to me it is a strange Perugian, with little interest for the Egyptian god compared to his covet for entering inner circles of a certain world. Their internal motivation is “I want to see how the lords sit at the table”. But in there [Masonry], you see, there are also good Christians and good Communists; as has always happened in this province, which has the art of living together in its genes”.
[”¦. ]
This month ““ Jan 2013 ““ the Italian press returned to the topic of the case again in a few brief articles. This time it was because of Sollecito’s book.
After Maurizio Molinari’s report from New York on the book in September, and the busting by Bruno Vespa on Porta a Porta of Francesco Sollecito, who ended up openly contradicting his own son’s statements, another hint appeared in the local press about what is cooking up backstage.
This article in Perugia Today has a neutral take, but the same understatement and kind of vagueness as it anticipates that something very likely will happen.
What I find most delightful is the quotation marks in the title around the word “author” ““ journalist Nicola Bossi doesn’t believe for a moment that Sollecito actually wrote the book:
Meredith Case: “author” Sollecito at risk of criminal lawsuit
The recounts about an alleged negotiation in order to pin the main charges on Amanda Knox, and unproven violence by the Perugia Police are under target. Mignini is considering criminal lawsuit.
Written by Nicola Bossi ““ Jan 4. 2013
The Meredith case is not closed, and this despite books and movies almost tend to drop it after the acquittal in second instance of Amanda Knox and Raffaele Sollecito - who were convicted in first degree for the murder of the English girl that took place in Via della Pergola.
On upcoming March the 25th the Court of Cassation of Rome will have to decide on the request for a re-opening the trial, submitted by the Procura with the authorization of Public Minister Giuliano Mignini.
In the environment of the magistrates there is confidence about a [guilty] verdict that many ““ in Italy and in the USA - have heavily attempted to discredit. But from the same environments around them, they talk about a greatly serene Mignini making assessments about the next strategic moves, following the attacks directed against him ““ and against those in Law Enforcement who cooperated with him ““ contained in the book by Raffaele Sollecito.
An upcoming criminal defamation lawsuit is becoming more and more likely every day, especially about some particular paragraphs. The material published by Sollecito has already resulted in discussions and clamor above all about claimed negotiations [with the prosecution] aiming to shift the blame onto Amanda alone, to be rewarded with his immediate release.
But there are also accusations against the Police about violence during his interrogations. “If you dare get up and walk, I beat you up in a bloody pulp and I kill you. I leave you in a pool of blood”. This is what you read in the book “˜Honour Bound’ issued in the US, as what Sollecito attributes to the Perugian officers.
“They wanted me to lie so they could frame Amanda”: this is the premise of the claimed negotiations claimed to indirectly involve Mignini too, which he always denied. Allegedly this would have been enough to get [Sollecito] out from prison soon, leaving the American woman in trouble.
So, these are grave accusations which Mignini apparently does not intend to let go unpunished. The criminal lawsuit is likely to be filed earlier than the date of Cassazione [25 March].
Another small piece of news is this article below published in Leonardo and written by Valentina Cervelli:
It seems basically a “commented” version of the Perugia Today article. Cervelli adds a few polite lines on her own thoughts in this piece, published on the Bbooks page of Leonardo,it; this is my translation:
Is Raffaele Sollecito going be sued soon for “Honor Bound”?
By Valentina Cervelli - 6. Jan 2013
Are there troubles in sight for Raffaele Sollecito? His “Honour Bound” book is going well in the United States in terms of sales, but here in Italy it might be soon result for him in a lawsuit for defamation by the Law Enforcement forces and by the Public Minister Giuliano Mignini.
As we know already, in Honor Bound ““ My journey to hell with Amanda Knox and return Raffaele Sollecito has reconstructed the whole judiciary story from his point of view, telling in his autobiography what [he says] is his own truth.
On March 25 Cassation in Rome will decide on the [prosecution] request for the re-opening of the trial submitted by the Procura authorized by Giuliano Mignini, after the acquittal in the second instance of the two main accused, Sollecito and Amanda Knox.
The young woman has returned back to her country and we bet it’s going to be difficult, if not impossible, to get her back in our country even in case of retrial after Cassation and a possible conviction. But lets leave aside this possible dispute and lets focus on the book. In Raffaele’s book Mignini is iimplicated because he reportedly comes out discredited. In the material published by Sollecito in his book he even talks about alleged negotiations in order to blame Knox alone, obtaining in reward a quick release.
And what about the allegations of Police violence during interrogations? Of course we don’t get into the merits, but it seems obvious that parties that may be considered offended would tend to launch a counter-attack to defend their dignity and their work. At the moment no lawsuit has been submitted. But with much probability that will be done before the decision of Cassazione.
By now we can only wait for the publishing of the book in our country, in order to assess with our minds what Raffaele Sollcito has written and the “hot” material published in his made-in-the-US autobiography.
By the way; one thing Valentina Cervelli might get wrong is the purported good sales of Sollecito-Gumbel’s book.
The Amazon.com site is reliable as quick indicator of a product’s success; the price of a new copy of “Honor Bond” on Amazon.com is now $ 3.51 (last week it was 3.76; the cover price is $ 24). It suggests sales are not quite as expected. The drop speed is significant if you consider that the book has been out for only four months.

[Above: the Florence Palace of Justice]
While many honest magistrates seem to be working in Florence, there is still some strange behavior by one or two people in the Florence prosecution office.
Iin particular by the chief prosecutor there were some unexplainable decisions. As people reading this site know, Giuliano Mignini and Michele Giuttari were convicted (of some of the charges) in the first degree trial in Florence.
The motivations document was disconcerting because: besides the proof of their innocence on the main charge, what was described as the evidence on the remaining charge constituted extremely weak and vague arguments for what was claimed about Giuttari, while they were totally non-existent about Mignini.
In the second instance appeal as we know the court completely crushed the trial case.
The case against them collapsed not because of a technicality, as the FOAs falsely claimed. In the figment of their imagination the Knox supporters erroneously thought that the Florence court had an “option” to overturn the case, to find Mignini and Giuttari innocent, but that they instead decided to pass the judgment on to some other tribunal.
The pro-Knox believers are probably also ready to believe blindfolded that there was some kind of evidence against Mignini.
The Knox believers are wrong. What in fact happened in Florence is something almost unique in a judge’s career. The first remarkable event was the decision by the Florence court of nullifying the first degree verdict. They did not simply overturn the verdict (neither change, or “reform” it as we say) since an overturning would imply acceptance that a previous verdict actually existed and was legitimate.
The cancellation was in fact an in limine act about the validity , which does not require an assessment about it correctness. The court went way beyond. In fact they nullified the whole trial, not only the previous one in terms of judgment, but also the preliminary hearing, and the indictment; and even the request of indictment.
It is a legal outcome not comparable to a simple change or overturning because it is a ruling that the whole proceeding was illegitimate from the very roots. The investigation itself of Mignini and Giuttari was declared illegitimate.
If elements were found for the opening of an investigation, the prosecutor would be entitled to carry on their duties, though the investigators should be from another territory. This is important because the Florence court found evidence that people from the same office were involved in cases against Giuttari and Mignini, both as offended parties and as prosecutors.
Because of a basic conflict of interest, the local prosecutors were incompatible and the Procura of Florence had no jurisdiction. Not even Genoa would be compatible.
Florentine prosecutors therefore had no right to bring cases against Mignini and Giuttari. The investigation files now must now be sent to the competent jurisdiction ““ where they should have been sent from the beginning ““ which is Turin; there other legitimate prosecutors will decide if and how there is anything to investigate about, and if there are any charges to bring against anyone. The Florentine trials should have never taken place. The court ordered that the legitimate investigators are the Procura of Turin.
In addition, they also ruled that the court of Florence would be an incompetent jurisdiction in any further possible case that stems from that investigation: since the competent prosecution is Turin, in case elements for the indictment of anyone for any charge are found, in the future, everything should go to a court in Turin ““ this, only if there will be any charge to bring to court .
This decision in Florence was a total debacle for the Florence prosecutors. It is in fact “politically” much worse than an overturning of a verdict. It is not just a like a different conclusion on the merit, it is the decision to take away even the investigation from them, a kind of implicit censure of their work as highly illegitimate.
But at this point in the procedings, something even worse and even more strange happened. The Procura of Florence did something even more unusual, in fact unprecedented as far as I know.
Apparently the Florence prosecutors are not happy at all to pass the investigation file on to Turin. For some reason they seem instead to want to do unnecessary and irrelevant hard work instead. The Florentine prosecutors impugned the decision and revisited this at the Supreme Court against the Florentine judges.
This step is almost unheard of because the decision of the Florence appeal court is of a type that manifestly cannot be impugned at the Supreme Court. The recourse is obviously going to be declared inadmissible. If that submission was done by a private citizen, they would get a heavy fine for that.
Here it is a power in the Florence judiciary branch making this inadmissible move; for unknown reasons.
I’d like to know the real motive behind the latest Florence move, the only effect of which can be a waste of time (and money), a delay, of at least one or maybe two more years, which only makes the failure of the whole proceeding against Mignini and Giuttari more likely due to lapse on an expiration terms.
I say “I’d like to know” but in fact one motivation stands out as obvious: the whole proceeding against Giuttari and Mignini, from the first bringing of the charges at the lower courts, appeared as having a wasting of time among its purposes.
One practical effect - maybe a practical purpose - of pushing the charges against Mignini, was taking the file about the Monster of Florence case links with the Narducci case away from Perugia. By this move, the Florentine prosecutors managed to factually put their hands on the Narducci-MoF file and remove it from the investigating powers in Perugia.
Another effect of this was delay. Now this latest move looks as if its purpose were to delay, as much as possible, the transfer of the legal documents to Turin.
What is the ultimate event that, by all this, they seem to be seeking to delay? I can’t know for sure, I can only guess; in fact, I have only one answer, which also stands out as something obvious for those who know a bit of the backstage:
Giuliano Mignini is not an ordinary magistrate, he belongs to the Anti-Mafia Territorial Division of Umbria, and recently was selected for a further promotion by the Supreme Council of Magistrates.
In fact what is delayed is the advancing of Mignini’s career: in fact he has been already promoted to a directive function; but, by the rules, his taking the post was frozen while awaiting the outcome and conclusion of the Florentine prosecution.
Prosecutor Mignini is de facto already functioning as a prominent Magistrate in Perugia and considered as such; but formally he has not been given the directive power. Several people ““ among them Spezi and a number of his journalist friends, but possibly also other much more important people too ““ are likely not at all eager to see Mignini awarded further power.
About the latest endeavor by Raffaele Sollecito, who became liable for criminal defamation by writing false allegations about Mignini and others in his book, I expect - as logically unavoidable ““ that several powers and subjects will basically have no option but taking legal against him.
There will be a strategic necessity to doing this in order to prevent extradition issues in the future, but also, above all, on principle, because Sollecito made false claims about public institutions that needt to have their names cleared. Considering the kind of allegations against the judiciary as an institution, and considering that Mignini is a judge of the Anti-Mafia Division, this is the kind of lawsuit that I see as likely to be submitted on a national level, in Rome.
If that is the case, it would not be the only strange thing that the courts of Rome will deal with.
It seems like there is a kind of “curse” on proceedings related to the Narducci case. All sections of the Supreme Court which have been asked seem to have attempted to declare themselves “˜incompetent’ about re-opening the cases related to the Perugian doctor. The Cassazione is a huge office with a hundred judges working there, but maybe not so many of them are eager to deal with this case.
This could be only a coincidence. It only brings up to my mind, through a free association of thoughts, a more generic question ““ a personal question of mine ““ that is whether the words “Masonry” and “Politics” have an echo in Roman corridors too.
*****
Finally I want to add another significant piece of Italian news.
The news a week ago was that the Procura of Florence is investigating a possible corruption/mafia plot involving construction enterprises and politicians that revolves around the building of a new high speed railway in Florence.
Some 31 people are being investigated and among them is the former governor of Umbria. A huge drilling machine ““ nicknamed the “Mona Lisa” ““ used to dig subway tunnels in Florence was sequestrated by the Procura.
In the last couple of years Perugia’s prosecution office had a main role in fighting political corruption, but it seems that the Florence Anti-Mafia division is also active, just as it was in the times when the prosecutor Vigna worked with them.
Vigna was the one who first evolved the “secret sect” scenario in the Monster of Florence case, raising unexpected problems among the Procura staff.
Thursday, August 16, 2012
An Overview From Italy Of The Galati-Costagliola Appeal To The Supreme Court Of Cassation
Posted by Machiavelli
Dr Giovanni Galati is the Procurator General of Perugia, and one of the two magistrates at the highest function currently working in the Region of Umbria.
Until early 2011 he worked in Rome as a Procurator General at the Supreme Court of Cassation in Rome. His life and career had nothing to do with Perugia. A native of Calabria, he spent the last and most important part of his career in Rome, and moved to Perugia only quite recently.
Working as a deputy chief prosecutor at the Supreme Court of Cassation, he developed an expertise as a “cassationist” magistrate. That means specialized in legitimacy issues, and in this role he handled several high profile cases. Among them was the recent one of Salvatore Cuffaro, the former governor of Sicily, now in jail.
Cuffaro was convicted for having favored the mafia and was sentenced to seven years. The governor was found guilty by the appeal court, but Galati impugned the sentencing by the Supreme Court on one specific aspect: while he agreed Cuffaro was guilty, he considered there was only evidence of common crime, while the lower courts failed to provide the legal requirements for proof of the aggravating circumstance of the mafia-related kind of crime.
In Galati’s opinion, Cuffaro was still corrupt and a criminal, and the difference may seem like a minor detail. His conclusion was not to overturn the verdict, but only to reduce the aggravating circumstance and shorten the prison term. Galati made the point and won, the Supreme Court cut one and a half year off Cuffaro’s prison term.
One thing to note is that the majority of Galati’s recourses are appeals in favor of the defendant. The Prosecution General, the office that brings cases to the Supreme Court, deals with procedure and legitimacy issues. Its aim is to ensure consistency and quality of work of the criminal courts.
It does not deal directly with the merit of evidence, but in fact, since the assessment of the evidence is a matter of internal logical consistency and consistency with trial actions, as well as respecting of procedure and of Supreme Court jurisprudence, the scrutiny of the lower court’s process obviously indirectly involves an assessment of the quality of evidence, and on the quality of the lower court’s reasoning on all factual points.
Giancarlo Costagliola was of course the lead prosecutor for the Hellmann-Zanetti appeal.
2. About the appeal
The Galati-Costigliola appeal is a 112-page document, with citations in an appendix to each chapter remanding to trial documents (technically the cited documents have to be considered included in the submission). The Supreme Court of Cassation however will have the entitlement of going through the whole trial documentation.
The Galati-Costagliola Appeal to the Supreme Court immediately looks different in quality and content from the previous court documents that we have seen up to now on the case. As we read it in Italian, it looks well written (except for a few grammar mistakes in the Latin parts) and stylistically homogeneous.
It dedicates extensive parts to the philosophy of law, and it includes several quotes of Supreme Court jurisprudence in the introductory and conclusive chapters.
It is an unusual appeal. Contrary to most appeals submitted by Galati as Procurator General, this one does not raise objections simply on parts of the sentencing, conclusions, or points of reasoning. Instead it attacks the verdict in its entirety. It attacks indeed all logical points and conclusions, including the part about calunnia, for which Knox was found guilty. And it goes even beyond.
Besides disputing the single points on the merit, it contains an explicit and more general attack on the whole appeal court’s approach to the case, against the general quality of their reasoning and their handling of trial and procedure, as well as against even their behavior even before the beginning of the trial discussion. There is an introductory part, and one conclusion part, which are dedicated to this kind of general criticism toward the entirety of the judges’ work.
At the beginning the document presents the summary of the ten reasons for appeal which, in Galati-Costagliola’s opinion, fatally affect the legitimacy of the judgment.
The ten questions of merit are the following:
1. The illegitimacy of Hellmann’s admission of new expert witnesses (Vecchiotti and Conti). The appointing of new experts violates the code. Galati-Costagliola clearly explains why, using both Supreme Court jurisprudence and Criminal Procedure Code. It addresses and shows the multiple instances of lack of reasoning in Hellmann’s explanations on the point, the “contradictory nature of reasoning” and its “manifest illogicality” in light of the law.
2. The failure to acquire elements of evidence. Galati-Costagliola focuses specifically on the rejection of witness testimonies, above all 1) the refusal to again hear the witness Aviello, and 2) the refusal of new tests on the knife. These decisions were taken in violation of Articles 190, 238 paragraph 5 and 495 paragraph 2 of the Criminal Procedure Code, and in violation of Article 606 (c) and (d) of the Criminal Procedure Code. There is manifest illogicality of the judgment on the point.
3. The establishing of the unreliability of the witness Quintavalle. The method declared to assess reliability of the witness violates the jurisprudence of the Supreme Court on the topic, and the insufficient reasoning violates Article 606(b) and (e) of the Criminal Procedure Code.
4. The establishing of the unreliability of the witness Curatolo. The reasons expressed are illogical, prejudicial, and violate the Criminal Procedure Code.
5. The claimed timing of the death of Meredith Kercher demonstrates a manifest illogicality in the reasoning, contains an unfounded assessment, and is manifestly in contrast with other court documentation of the case. The internal and external inconsistencies of Hellmann’s statements on the topic constitute a violation of the Criminal Procedure Code.
6. The genetic investigations: coverage of this topic in Hellmann’s sentencing report demonstrates deficiency in the reasoning, and inconsistency and illogicality [Article 606(e) Criminal Procedure Code]
7. The analysis of the prints and traces (stains) demonstrates deficiency in the reasoning, and a contradictory nature and illogicality in the reasoning [Article 606(e) Criminal Procedure Code]
8. The presence of Knox and Sollecito at Via della Pergola on the night of the murder: misrepresentation of the evidence presented is demonstrated and illogicality of the reasoning [Article 606 paragraph 1(e) Criminal Procedure Code]. Violation of procedural rules and illogicality of the reasoning [Article 606 paragraph 1(b) and (e) Criminal Procedure Code] are demonstrated.
9. The staging of the break-in (simulation of a crime): demonstration of deficiency in the reasoning and manifest illogicality of the same [Article 606(e) Criminal Procedure Code]
10. The exclusion of aggravation in the calunnia offence: the contradictory nature or manifest illogicality of the reasoning is demonstrated, also defects resulting from internal and external inconsistence with the court documents of the case: starting with the declarations by Patrick Diya Lumumba, and those by the accused, Amanda Knox, and the contents of the conversation between the latter and her mother on 10 November 2007 [Article 606(e) last part, Criminal Procedure Code].
However, the ten reasons listed above are not all of Galati-Costagliola’s arguments. Their explanations cover the core (80%) of the Hellmann-Zanetti sentencing document. But even before entering into these reasons on the merit, Galati-Costagliola make a preliminary point, a “premise” to the whole document.
The “premise” takes twenty pages and this alone is telling about the gravity of the criticism Dr Galati is going to make throughout the whole appeal document. The premise warns the readers (the judges of the Supreme Court) that in fact there is a problem of quality pervading the whole of Hellmann’s and Zanetti’s work which affects deeply their reasoning and conclusions on multiple occasion and in multiple concurring ways.
He makes clear that his criticism of Hellmann is methodological, and he points to the trial as a whole from the roots, far beyond the single topic of errors exposed in the appeal.
The “premise” of preliminary points, a short essay in itself, has its own summary of six points, each one to explain a typology of recurrent error committed by Hellmann and Zanetti. In the premise Galati explains four of the types of error, while the last two are discussed in the further chapters together with some of the points on the merit.
These are the six types of error:
1. One error “of method” affecting the logical process is the “petitio principii”, which Galati-Costagliola addresses as a recurrent, structural and pervasive method of reasoning used by Hellmann-Zanetti.
It is “begging the question”, a kind of empty circular reasoning. This is demonstrated in several chapters and points. For Hellmann-Zanetti’s reasoning, Galati-Costagliola reserve the names “paradoxical”, “disconcerting”, “useless”, “circular”, and worse in this same tone.
2. The failure to apply the inferential-inductive method to assess circumstantial evidence. This is a key point based on jurisprudence and is in fact a devastating general argument against Hellmann-Zanetti:The appeal to Cassation’s jurisprudence on the circumstantial case originates from the fact that the Assize Appeal Court did not deploy a unified appreciation of the circumstantial evidence and did not examine the various circumstantial items in a global and unified way.
With its judgment it has, instead, fragmented the circumstantial evidence; it has weighed each item in isolation with an erroneous logico-judicial method of proceeding, with the aim of criticizing the individual qualitative status of each of them ..
Dr Galati accuses the appeal court of focusing on the quality of some pieces of circumstantial evidence, instead of their correlation to each other as the Supreme Court always requires. .The appeal judges, in actual fact, deny that the probative reasoning and the decisive and cognitive proceeding of the court is to be found in the circumstantial evidence paradigm of the hypothetico-probabilistic kind, in which the maxims of experience, statistical probability and logical probability have a significant weight.
The court must reach a decision by means of the “inductive-inferential” method: it proceeds, by inference, from individual and certain items of data, through a series of progressive causalities, to further and fuller information, so arriving at a unification of them in the context of [13] the reconstructed hypothesis of the fact.
This means that the data, informed and justified by the conclusions, are not contained in their entirety in the premises of the reasoning, as would have happened if the reasoning were of the deductive type “¦ (..) A single element, therefore, concerning a segment of the facts, has a meaning that is not necessarily unambiguous.
Dr Galati cites and explains further:
The Perugia Court of Appeal has opted, instead, precisely for the parceled-out evaluation of individual probative elements, as if each [14] one of them must have an absolutely unambiguous meaning, and as if the reasoning to be followed were of the deductive type.
This error emerges from the text of the judgment itself, but the gravity of the error committed by the Court in its decision derives from the fact that even the individual elements had been acquired by the cognitive-decisioning process in a totally partial manner, isolating the sole aspect that allowed the recognizing of doubts and uncertainties in the element itself..
So Galati-Costagliola concludes ““ and this by now is obvious ““ that the Hellmann-Zanetti court followed a “deductive only” paradigm on pieces in isolation, instead of the “inferential-inductive” paradigm prescribed by Supreme Court requirements (1995).
Moreover, Hellmann-Zanetti applied a deductive paradigm of assessment only to some cherry picked aspects of the single isolated pieces of evidence, overlooking other qualities of the single piece (an example ““ my own ““ is the possible “contamination” of the bra clasp found on the floor in the murder room.) Ordering an assessment of the quality of any element as if it was a proof in isolation from the rest of the evidence is itself unlawful.
But Hellmann”“Zanetti also picked out of the evidence one aspect alone, for example it points to the theoretical possibility of contamination by touching from gloves, but does not consider the negative check results from the possible contamination sources. The interpretation of X-DNA from the bra-clasp by Vecchiotti in the conclusion is worded as if to ignore the results on the Y-haplotype, and so on.
So even single aspects/qualities of isolated items are further isolated from other aspects by Hellmann-Zanetti, and are assessed without looking for a relationship to the context. This is a core violation of the basics of jurisprudence in cases based on circumstantial evidence.
3. Refusal to acquire documentation as evidence: the definitive Guede verdict. Hellmann-Zanetti refused to acquire the documentation and to consider it a piece of evidence, without any backing from procedure jurisprudence and without providing any justification.By doing this the Hellmann court was again violating the legal boundaries. The Galati-Costagliola appeal considers this as one more type of violation, the refusal to attribute any kind of probative value to the definitive verdict on Guede, thus violating Article 238 of the Criminal Procedure Core, and bringing up a manifestly illegitimate justification. The violation is quite egregious under the code.
4. Failure to assess and to weight key elements, among which is Knox’s written “memoir”. This is a severe violation of article 237 of the Criminal Procedure Code.The usability of Knox’s “memoir” as well as its probative value were already established by the Supreme Court itself, and it was admitted into the process. Hellmann-Zanetti fail to provide the slightest logical explanation for changing the established assessment and disregarding that evidence.
5. The failure to acquire possibly important pieces of evidence. Galati-Costagliola are focused mainly on two points: 1) the knife, and the refusal of having it further tested for DNA; 2) the refusal to hear Aviello after his retraction of his claims.We know that, while the testimony of Aviello might be just not credible because of his proven unreliability, and while some may argue that thus his testimony was not “decisive”, the testing of DNA found on the knife would be a piece of evidence for sure.
But the Procurator General points out that the refusal to hear Aviello is part of a severe violation, because the Hellmann motivazioni accepts his retraction statement, considering it thus reliable, but throws out some parts of it and refuses to hear him as a witness.
So the Galati-Costagliola appeal statement includes quotes of some shocking lines from Aviello’s interrogation, to show the heavy nature of it that cannot be thrown out without assessment
A twisting of words - like “cutting-edge” which becomes “experimental” in Hellmann’s reasoning - is the illogical justification for Hellmann-Zanetti forbidding a further DNA test. The motivation is obviously bogus, and Galati backs the point with quotes from Novelli’s tehnical explanation.
6. Galati-Costagliola address a pervasive violation, claiming it recurs multiple times in the document: a violation of a kind called “misrepresentation of the evidence”.This is when the judge omits aspects of the pieces of evidence that would contradict their conclusion, expressing an obvious cognitive bias. The appeal describes this violation in different chapters (5,6,8) as occurring in the process of assessing different pieces of evidence, including witness reports, wiretappings, and other items.
3. My own assessment of the Galati appeal
As you can guess from the summary above, the appeal is rather strong, and explains many heavy implications in Italian jurisprudence so that it would be difficult for the Supreme Court to reject it.
Difficult not only because the kind of objections raised by Galati-Costagliola are devastating to Hellmann’s legitimacy (in fact it’s even more, they tend to form a picture of manipulation of the trial); and not only because Hellmann’s verdict appears to be devastating to jurisprudence generally, so much so that it would become impossible to rule on guilt in many other cases; and not only because a verdict that puts together the conviction for calunnia (a felony crime with malice) and the acquittal for murder, has a contradiction on a macro-level.
But also diificult because the same office of Cassation has already issued another definitive verdict, on the Rudy Guede case. They acknowledged that Guede did not act alone, and the Supreme Court themselves even obtained independently some elements of evidence of this, which had not been considered by the previous judges.
Accepting Hellmann-Zanetti and rejecting Galati would equate to cancel Guede’s verdict. It would require a re-write of the entire process from scratch.
Galati-Costagliola shed light on many points in good order, so I tend to be optimistic and confident in the strength of the appeal.
However I also believe there could have been something more, to make it even more strong. There are a few points ““ in my opinion - still missing, which I would have added. Four points that I miss are the following:
1. There is no mention about the analysis ““ or the lack thereof - of Knox’s lies, aka the inconsistencies in her story, her “mop-shower” alibi version, what she told prior to her false accusation. There was a partial analysis of this area of evidence in Massei, who only mentioned her lying about her behavior before Meredith’s closed door.
But a lot more could have been brought out, so many contradictions and so sharp, to demonstrate that her recollection was entirely fictional. The entire topic disappeared in Hellmann’s logic and Galati-Costagliola does not hit on the point. I think this obliteration of key evidence should have been a battlefield for the appeal, I think it could have been linked to the error of misrepresentation of the evidence.
2. Galati-Costagliola misses one point of criticism on the bathmat footprint assessment. It does make a point objecting to the manifest illogicality of Hellmann’s reasoning on the footprint analysis. But there is one point more where it could hit, one external inconsistency that could have been highlighted:Hellmann-Zanetti’s illogical reasoning on the footprint is based on a false assumption. Not only it has no basis in the acts of evidence but it is proven false. It is that Hellmann excludes Sollecito on the basis that the print was “inked” by stepping on a flat surface (proven false), and attributes it to Guede, on the opposite assumption that it was produced by immersion. I note that Galati does not address directly this introduction of false premises.
3. The appeal deals only partly with the Vecchiotti-Conti report controversy. It points to Hellmann’s contradiction on “contamination” of the knife and their failure to indicate any path for any contamination in general. But it does not say much about the bra clasp (it implies however that Sollecito’s DNA was found).Vecchiotti’s report is unacceptable when it comes to the DNA chart: it acknowledges that Sollecito’s DNA was on the clasp after all when it comes to the Y-haplotype, but in the autosome-chromosome analysis attempts to create confusion by applying principles that are incompatible with Supreme Court guidelines on evidence analysis. Also Vecchiotti desecends into inconsistency and shows her real cards when she attempts to figure out contamination paths for how Sollecito’s DNA had arrived on the clasp.
However, I think the SCC might have all the material on this point in the attachment documents from Galati.
4. One missing point important to me is that Galati-Costagliola does not point out the prejudicial and racist stance declared at the beginning and at the core of Hellmann’s reasoning.Other parts are maybe more outrageous and more directly offensive to other people and other intelligences, but the racist Hellmann’s reason to me is the most disgusting.
It is a shame that a judge of the Republic is allowed to write things like this. Hellmann-Zanetti write that it is itself “unlikely” ““ it would require a very special proof ““ that Guede and Knox/Sollecito could have just met and done something together because they are “different”, while Sollecito and Knox are “good fellows”
Hellmann-Zanetti could have legitimately used the argument that it was likely for Guede to have committed a crime alone because he had a police record. They could have used this argument, but they did not use it. Their wording was totally different. I think we can guess what the reason is why they didn’t use this argument. It would have been extremely weak.
There is a logical connection between a theoretical break in and the theft in the law firm; this logical connection is equal to (in fact much weaker than) the logical connection between a staged break in and a roommate. But there is no logical connection between crimes like a theft of a laptop in an apartment and assaulting, torturing and killing a woman: thousands, in fact hundreds of thousands, of common thieves, in Italy, do not rape and do not kill anyone.
You cannot use the criminal record of Rudy Guede as a basis for claiming it is “likely” that he could commit a crime of this kind alone. That’s why Hellmann-Zanetti didn’t use it.
Instead, they used prejudice, the racist card: instead of trying to explain why it was likely that Rudy could have done it alone, they decided to claim that it was unlikely that they would find themselves together, because they are “good fellows” (and “different”).
As you can understand, this has nothing to do with Rudy’s criminal record.
By the way, Hellmann-Zanetti know that Knox had been knowing Guede long before she became friends with Sollecito, they already knew that Knox and Guede have been seen together on more than one occasion in more than one place, and even that Guede in fact attended the cottage and was friends with other people in the cottage. In fact they knew Guede and Knox used to attend the same places, house, roads and pubs.
They also knew that both Sollecito and Guede attended Piazza Grimana and the drug circle (which is the square in front of the school where Amanda had her language classes), that they lived 150 meters from each other, walked every day the same road; and ate at the same bars.
It was also known that not only Guede alone, but both Knox and Sollecito had questionable aspects in their personalities, so that these 20-years olds were not exactly expressing a profound stability in their lives.
They knew details like: leaving university, abandoning a job after one day, public disturbance fines, drunk parties, pouring beer glasses on the heads of unknowns, flirting with clients, relational problems with roommates and other girls, bringing several men at home causing arguments with roommates, collecting violent porn, heavy drug abuse over the years, knife collecting, a possible suicide mother, a lonely childhood and introverted character under the attention of a college director, memory voids.
Nobody is perfect. These details do not mean someone is guilty of anything. But what exactly is, in Hellmann-Zanetti’s mind, the “difference” of these personalities that makes these two be so obviously “good fellows”, as opposed to Guede, to the point that it is “extremely unlikely” that they can be found together, despite the fact that they attend the same places every day?
Who can tell me what is the possible reason of this difference?
Maybe there could be a relation with the fact that in Italian “good fellows” ““ “bravi ragazzi” means, in the subtext ” my family” as opposed to the other who is an outsider.
To my eyes this reasoning of Hellmann-Zanetti turns them into individuals who deserves no respect, they gain with this the most justified contempt, they should be treated like pigs: they practically wrote “they can’t be around together with Guede because they are our friends” while “he is out”.
Two bastards dirtying my country by wearing the robes of judges. I find this disgusting. It is unfortunate that Galati-Costagliola overlook this point.
4. The Galati appeal: my final thoughts
It is not possible to understand in depth the 10 points of merit from my short summary, which in fact is just a list. By reading them, I think they show their inner logical strength. I found only one weakness, that is in one of the sub-sections of point 5, where Galati-Costagliola discuss about Guede’s skype call.
I feel it’s remarkable that I couldn’t find any other questionable point (I am rather severe).
Reason 8 appears made of several points each with a different topic. They didn’t seem especially important to me as pieces of evidence, however they exist and are part of Galati-Costagliola criticism of Hellmann’s reasoning.
Reason 9 is effective but I would have used much more extensively the elements of evidence available and place them in line before the judge’s faces. Galati-Costagliola prefer to direct their objection to the inconsistence of Hellmann-Zanetti.
The part where Galati sounds more outraged is Reason 10, about the Calunnia. In this part in fact Hellmann sounds most “FoA” and offensive. In fact I think I have never read before a Cassation recourse so scathing as the Galati-Costagliola document seems to be on the Hellmann’s report.
Reading through the whole Galati document in Italian, you come upon expressions addressing the lower court’s work (repeatedly) with terms like “grave error” and “grave behavior”, you find also “disconcerting shallowness”, or the accusation of “ignoring the law”.
In the C&V report section Galati-Costagliola have some sarcastic lines such as: “how is it now they suddenly have become experts?”. In other parts you read the word “prejudice” or “obvious bias”, some of the parts of the Hellmann-Zanetti report are called “offensive” and “gratuitous”, and you also encounter the term “insinuation”.
Galati-Costagliola devolve significant attention to their method error in logic called “petitio principii”. Now, in the traditional scholarly logic, there is a list of thirteen kind of typical “logical errors” divided in three groups: the errors of the kind “fallacia in voce” (due to misusing words in their meaning concepts) , “fallacia in re” (about getting facts wrong in the direct logical use of them) and “fallacia in deductione” (error in inference process): there are four types of “fallacia in re” and five types of “fallacia in deductione”.
The “petitio principii” (implicit circular reasoning) is one of the five types of “fallacia in deductione”. Galati-Costagliola focus on this and on another case of “fallacia in re” called “corax”, but in fact in Hellmann-Zanetti there are also severe cases of logical errors of other kinds of “fallacia in deductione” and of the kinds of “fallacia in re”. Which may not matter too much.
This was my final thought. I hope this can help readers to gain a rough idea of what the Galati-Costagliola Appeal to the Supreme Court looks like, its structure, its kind of arguments, and assess its qualities.
If the Supreme Court of Cassation accepts the appeal, I would consider the battle for justice in this case as won. I know that the Kerchers may need to see the end of the whole process. But to me, the fact of having the Galati-Costagliola appeal means itself half victory achieved.
This document, as you know, was issued by the highest magistrate in Umbria and what will remain in history is the forcible assertion that Knox and Sollecito are murderers beyond any doubt as expressed by Dr Galati in this document and elsewhere, as well as his outrage for the disgusting Hellmann-Zanetti trash-verdict.
This stance will never go away.
Saturday, July 21, 2012
Ominous Development For Sollecito And Knox: A DNA Conviction Based On A Tiny Sample Of DNA
Posted by The Machine
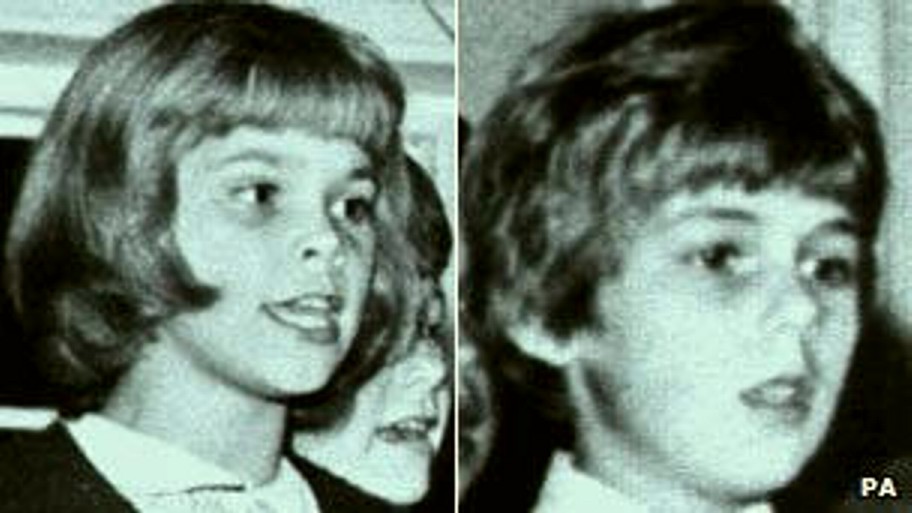

[Burgess, image below, murdered Yolande Waddington and, above, Jeanette Wigmore and Jacqueline Williams]
There is a HUGE dagger hanging over Sollecito and Knox. A UK case resolved this week indicates why.
New tests on the DNA sample on the large knife found in Sollecito’s house which the independent DNA experts refused to do, and the judges failed to re-order despite a strong prosecution request, could result in Knox and Sollecito being ultimately convicted and secure Knox’s extradition to serve out her term.
Lawyers consider it a dead certainty that the Supreme Court will order those tests - that is if they dont throw out the entire Hellman/Zanetti judgment for illegal scope, or throw out the DNA report for illegally having been ordered in the first place.
(1) Summary of the UK case
David Burgess this week was convicted in Reading of murdering Yolande Waddington, 17, some 46 years after the crime was committed, thanks to all the advances in DNA technology. Back then, he was already convicted of killing Jeanette Wigmore and Jacqueline Williams.
Burgess is the latest person in Britain to have been finally found guilty of murder years after his crime was committed. Nat Fraser, Gary Dobson and David Norris had been convicted of murder this year after evading justice for a number of years.
In September 2010, Thames Valley Police reviewed the case and with advances in DNA techniques finally gathered the evidence which resulted in Burgess being convicted of Yolande Waddington’s murder.
Forensic experts obtained a partial DNA profile from the blood samples using a new technique called MiniFiler. It differs from previous methods as it can obtain information from smaller pieces of DNA. This is ideal for older cases where samples have degraded over time.
According to the manufacturer’s website
[The MiniFiler kit] increases your ability to obtain DNA results from compromised samples that previously would have yielded limited or no genetic data. This means cold cases can come off the shelf for re-analysis and new, challenging samples have a better chance of delivering interpretable results.
When David Burgess attacked Yolande, he left blood on a number of Yolande’s items, including her hair band and comb. Tests showed the chances of the DNA found on the comb and hair band not being Burgess’s were not more than one in a billion.
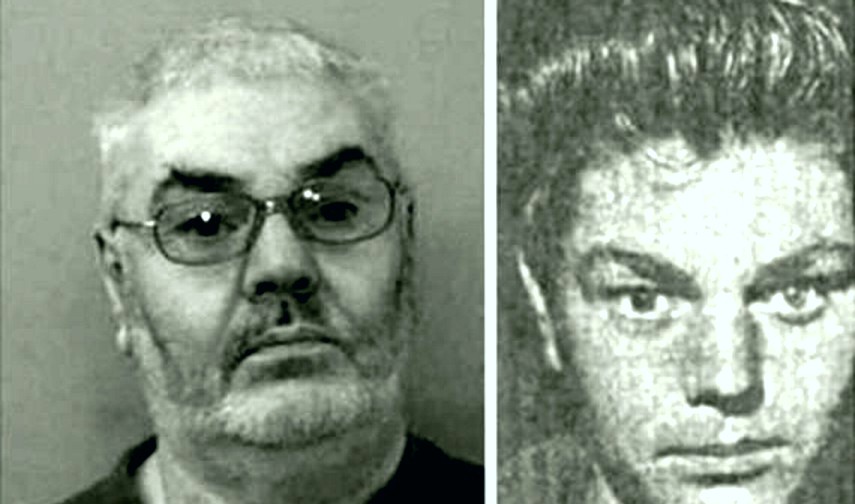
[Below: David Burgess then and now who had taunted the police a year ago to “prove it”]

(2) Here are the implications for RS and AK
It puts the 46-day delay (caused by the defenses) in retrieving the bra clasp into perspective.
It’s not the first case of somebody being convicted of murder decades after the crime took place on the strength of DNA evidence. Ronald Castree was convicted of murdering Lesley Molseed 32 years later.
It also highlights the arrogant negligence of the DNA consultants Stefano Conti and Carla Vecchiotti who had refused to carry out ordered test on the knife for flimsy reasons (“the technology is experimental” when it wasn’t) that no US or UK court would have accepted. They had been specifically instructed to do the tests if possible by Judge Hellmann.
At trial in 2009 it was accepted that Amanda Knox’s DNA was found on the handle of the knife sequestered from Sollecito’s kitchen. There still is no argument about that.
And a number of independent forensic experts - Dr. Patrizia Stefanoni, Dr. Renato Biondo, Professor Francesca Torricelli and former Caribinieri General Luciano Garofano - had all confirmed that Meredith’s DNA was found on the blade.
Even Greg Hampikian, a forensic expert who argues Knox is innocent, concedes that Meredith’s DNA was definitely found on the blade.
Stefano Conti and Carla Vecchiotti didn’t know that Dr Stefanoni analysed the traces on the knife a long six days after last handling Meredith’s DNA. Contamination couldn’t possibly have occurred in the laboratory after so long a gap.
At the appeal, Professor Guiseppe Novelli testified that there are a number of laboratories that now have the latest accepted technology to carry out a new test on the remaining DNA on the knife.
The fact that Judge Hellmann denied the prosecution the opportunity to present evidence to the contrary was a violation of the procedure code. Italian law states the following:
If new evidence about a point is admitted, evidence a contrario proposed by the opposing party must always be admitted too.
Dr Giovanni Galati has now argued in his appeal to the Supreme Court that Judge Hellmann should have allowed a new test to be performed because the technology is NOT experimental but cutting edge. Summary here:
The second [point concerns] the decision to not allow a new forensic investigation requested by the prosecution at the end of the ruling discussion. In the appeal to Cassation it is written that the Appeal Court’s rejection reveals “contradictoriness/contrariness and demonstrates manifest illogicality in the grounds for the judgement/reasoning report”.
As remarked at the top, if the entire judgment or the DNA report are not thrown out for illegal scope, Judge Hellman’s refusal to allow the prosecution’s request to allow a new test on the knife will be the main reason why his verdict will be revoked.
Under Italian law RS and AK still stand accused until the Supreme Court signs off. Anyone who is concerned with the truth and justice and what Meredith stood for and the good name of Italy will want to know whether the remaining DNA on the knife is Meredith’s.
If Meredith’s DNA is identified on the knife it should make conviction and extradition a slam dunk..
[Below: ViaDellaPergola’s video first posted 18 months ago and still relevant]
Thursday, July 19, 2012
This Formidable Prosecution Appeal To The Supreme Court Is Placed On The Agenda Next March
Posted by Peter Quennell

The Associated Press once again reveals its strong systematic anti-Italy bias in reporting the scheduling of the appeal.
Its headline on the report it sent out to thousands of its owners the media outlets reads “Amanda Knox Case: Acquittal Appeal Set For March By Italy”
Huh? That is the guts of the thing?
Well, hardly.
First, defense chances are slim, as there is no question that Knox did point falsely to Lumumba. On tape she even admitted that to her own mother, and her various explanations on the stand at trial simply dropped her in it some more.
That defense appeal could be dismissed in a sentence or two. It is simply grandstanding.
And second, vastly more importantly because this could lead to a complete retrial back in Perugia the AP headline and story should have fully explained the real 80,000 pound gorilla in the room.
This is the appeal that the Chief Prosecutor for Umbria Dr Galati has filed. The Associated Press has never told the global audience either what is in the prosecution appeal or precisely who Dr Galati is. Not even a hint.
Dr Galati was a Deputy Chief Prosecutor at the Supreme Court and is one of the most powerful and experienced in Italy. Why was he not quoted in the AP’s story?
Here is the real story of his appeal that the Associated Press doesn’t seem to want the global audience to know. First posted here back on 14 February when Dr Galati called his press conference on the appeal.
Italian lawyers are already remarking that Dr Galati’s appeal as summarised below is as tough as they ever get.
In their view the Hellman report reads more like a defense brief than a balanced appeal-court outcome in a murder trial. Both judges were put on the case on mysterious instructions from Rome, suggesting that the minister of justice had perhaps been leaned on - the judge pushed aside was extremely annoyed.
Both Judge Hellmann and Judge Zanetti, while undeniably good judges in their own fields (business and civil), are vastly less experienced at criminal trials than either Judge Micheli or Judge Massei. The entry in the Italian Wikipedia describes them thus.
Although the Assize Court of Appeal was to be chaired by Dr. Sergio Matteini Chiari, Chairman of the Criminal Division of the Court of Appeal in Perugia, in circumstances not well understood Dr. Claudio Pratillo Hellmann, who chairs the Labor Chamber of the Court, has been called on to preside over the appeal court,
The judge to the side of the main judge, Dr. Massimo Zanetti, came from the Civil Section, and both had had limited experience with criminal trials both rather remote in time (only the cases of Spoleto and Orvieto).
Judge Hellmann’s announcement of the verdict on the night was very odd, suggesting he had been outnumbered and was embarrassed. Remarks he made the next day seemed to confirm that. The weak sentencing report is said to be not his work, and was written by Judge Zanetti.
The Supreme Court of Cassation could insist on a complete new appeal trial or a partial new trial in Perugia if it accepts any of Dr Galati’s arguments at all. His appeal statement appeal is in three tiers, and a reversal could be ordered at any tier..
1. The Hellmann Court’s wide scope was illegally far too wide
Italian judicial code is very clear on this. They MUST stick to just the appealed items and not wander all over the map. Judge Zanetti was quite wrong at the start to declare that everything was open except the fact that Meredith had been murdered.
2. The DNA consultancy by Stefano Conti and Carla Vecchiotti was illegal
Defenses had every chance to attend the Scientific Police testing the first time around. It was a slippery dodge to skip those tests and then slime them. They had every opportunity at trial to throw aspersions. They are not meant to shop around.
3. There are many problems of wrong logic, evidence, and witnesses
The Massei trial sat through weeks and weeks of skilled prosecution presentations of the evidence including the forensic evidence and the many witnesses. The Hellman court got to see almost none of this and heard mostly from the defense.
This translation is from Umbria24 by our main poster ZiaK.
Meredith case: the prosecution appeals to Cassation: the acquittal verdict should be “nullified”.
For the Chief Magistrates of the [Umbria] Prosecution, “it was almost exclusively the defence arguments which were taken heed of”
By Francesca Marruco
The first-level conviction verdict was “complete and thorough” while the verdict of the second-level is “contradictory and illogical”. For this reason, the General Prosecution of Perugia asks the Cassation to revoke or invalidate it.
“We are still extremely convinced that Amanda and Raffaele are co-perpetrators of the murder of Meredith Kercher” said the Chief Prosecutor of Perugia, Giovanni Galati and the Deputy Chief Prosecutor, Giancarlo Costagliola.
Verdict that should be revoked
“The second-level verdict should be annulled/revoked…. There are precise reasons for revoking it”, Mr Galati went on to say. In the Hellman reasoning report on the verdict with which the second-level judges acquitted the ex-boyfriend and girlfriend “there are so many errors, and many omissions. There is inconsistency in the grounds for judgement, which brings us to nothing.”
“It is as if they had ruled ex novo [anew] on Meredith’s murder” added the Deputy Prosecutor, Giancarlo Costagliola, “basing their decision solely on the arguments of the defence.”
“Normally the appeal judge evaluates the reasoning procedure of the first-instance judge and compares it to new elements. But this one missed that out altogether: there is no comparison between the checks carried out in the first and second instances. Only what was carried out during the appeal was evaluated.”
Only defence arguments were taken heed of
For the magistrates, in fact, the second-level judges “took heed, almost exclusively, of the arguments of the defence consultants or the reconstruction hypotheses that were largely to the benefit of the defense theses”.
The prosecutors who authored the appeal [to Cassation] also criticized the “method used”. “The first-instance verdict”, they wrote, “was summarized in just a few lines”,
“The verdict [which we] challenge completely ignored all the other aspects which corresponded with the accusation’s hypothesis, all the aspects which, on the contrary - as was seen in the reasoning report of the first-instance verdict - had been rigorously pointed out and considered by the Assizes Court [trial court] in its decision.”
“In examining the individual [items of] evidence, the challenged sentence has fallen into consistent procedural error in the weaknesses and evident illogicality of the grounds for its decision.”
Prejudice by the two appeal judges
For the General Prosecution magistrates, the second-level [first appeal] judges appear to have shown “a sort of prejudice” with the “infelicitous preamble of the judge [the author], who is supposed to be impartial”, when he declared that “nothing is certain except the death of Meredith Kercher”, which to the others [Mr Galati and Mr Costagliola] is nothing more than “a resounding preview/forecast of the judgement” and a “disconcerting” affirmation.
The ten points of the appealThe reasons for the appeal to Cassation which Perugia’s General Prosecution presented today against the acquittal verdict of Amanda and Raffaele are based on ten points of the second-level verdict.
The first is the lack of grounds for the decision, in the decree of 18 December 2010, to allow the forensic testimony/expert witness in the appeal judgement.
The second, in contrast, concerns a contrary decision: the decision to not allow a new forensic investigation requested by the prosecution at the end of the ruling discussion. In the appeal to Cassation it is written that the Appeal Court’s rejection reveals “contradictoriness/contrariness and demonstrates manifest illogicality in the grounds for the judgement/reasoning report”.
The other points deal with the decision by the Appeal court of Assizes of Perugia to not hear the witness Aviello, also the definition of “unreliable” [in the Hellman Report] with reference to the witnesses Roberto Quintavalle and and Antonio Curatolo, also the time of death of Meredith Kercher, also on the genetic investigations.
As well as the analyses of the prints and other traces, also the presence of Amanda and Sollecito in via della Pergola, also the simulation of a crime [the staged break-in], and also the exclusion of the aggravating circumstance of the crime of “calumny”.
Missing assumption/acceptance of decisive evidence
In the appeal to Cassation there is also mention of the “missing assumption/acceptance of a decisive proof”
In other words, of that proof [presented at trial court] which consisted of “the carrying out of the genetic analysis on the sample taken from the knife by the experts appointed by the Court during the appeal judgement, who did not carry out the analyses of that sample, thus violating a specific request contained in the [orders given to them] when they were assigned to the expert-witness post”
“In the second-level [Hellman] verdict”, the magistrates said, “the judges sought to refer to this in their own way, by speaking of an “experimental method” by which these tests/checks could be carried out.
But this is not the case”, said Deputy Chief Prosecutor Giancarlo Costagliola: “Dr Novelli [the prosecution’s DNA consultant at appeal] spoke of cutting-edge technology, not of experimental methods”.
Tuesday, February 07, 2012
Knox Team to Appeal Conviction And 3-Year Sentence For Framing Patrick Lumumba
Posted by Peter Quennell

[Above: the Supreme Court of Cassation]
Appeals against Judge Hellman’s rulings must be lodged in Rome by 18 February.
Now Reuters is reporting a Knox-team appeal apparently announced by David Marriott. The Knox team probably had little choice but to lodge this seeming long-shot of an appeal.
Judge Hellman’s ruling left her “half pregnant” facing a hard-line and unbendable Supreme Court and it left her mom and dad more vulnerable in their own trial for calunnia for claiming in a UK interview that Knox only “confessed” in fingering Patrick because of duress.
Explanation of calunnia
The charge of calunnia (art. 368) has been commonly translated as “slander” in the English/US media. This translation is incorrect, however, as calunnia is a crime with no direct equivalent in the respective legal systems.
The equivalent of “criminal slander” is diffamazione, which is an attack on someone”Ÿs reputation. Calunnia is the crime of making false criminal accusations against someone whom the accuser knows to be innocent, or to simulate/fabricate false evidence, independently of the credibility/admissibility of the accusation or evidence.
The charges of calunnia and diffamazione are subject to very different jurisprudence. Diffamazione is public and explicit, and is a more minor offence, usually resulting in a fine and only prosecuted if the victim files a complaint, while calunnia can be secret or known only to the authorities. It may consist only of the simulation of clues, and is automatically prosecuted by the judiciary.
The crimes of calunnia and diffamazione are located in different sections of the criminal code: while diffamazione is in the chapter entitled “crimes against honour” in the section of the Code protecting personal liberties, calunnia is discussed in the chapter entitled “crimes against the administration of justice”, in a section that protects public powers.
Judge Hellman essentially contradicted Cassation’s ruling on Guede which agreed strongly that Guede and two others did it (Judge Hellman of course went for the very tenuous lone wolf approach which Judge Micheli and Judge Massei both shot down in some detail) which had many lawyers in Italy doing double-takes.
Knox in fact fingered Patrick when she was merely a witness who had not even been invited to Perugia police headquarters for the evening and who had volunteered for the questioning.
The interrogators have all claimed she was under no duress except the duress of hearing that Sollecito in the next interrogation room had just called her a liar and destroyed the latest of her various alibis.
Then she had several weeks (as did her mom) to move to spring a devastated Patrick from an adjacent wing in Capanne prison, but of course she didn’t.
Her lawyers never lodged a complaint against the claimed duress and on the witness stand at trial in mid-2010 the prosecutors actually got her to admit that she was treated well.
Key at this stage may be that Knox cannot use her natural advantages of being young and rather dopey and of being able to speak up in court at any time, not under oath or cross-examination, which she used twice in front of Judge Hellman (with lusty sobs and tears for herself and no caring for Meredith).
Cassation works like Supreme Courts elsewhere in Europe and the United States They receive the written appeals and then months or even years later hold very brief hearings, and then almost immediately issue a ruling. It looks to us like the case almost certainly gets bounced back to Perugia - and a new judge - for re-working.
Judge Hellman may have found Patrick’s highly aggressive lawyer impossible to overrule, and he would have been wildly unpopular in Italy to leave Patrick without even his small settlement. If Patrick’s lawyer does not somehow react to this appeal it will be a surprise. He may have the opportunity for rebuttal.
This case has thrown up a lot of possibilities for shortening the Italian process in murder cases and leveling the playing field in favor of victims and families. We’ll round up and post ideas for such reforms already being pushed in Italy by reformers such as Barbara Benedettelli.
Reforms might include no right to defendant statements in court without the possibility of cross-examination, the limiting of judges’ scopes in first appeals, and no jury being required for those appeals.
But everybody sure appreciates those judges’ and juries’ written statements. A precedent the whole world could use.
Tuesday, October 11, 2011
Excellent Sunday Times Report On The Many Killer Questions The Second Appeal Next Year Might Answer
Posted by Peter Quennell

[Rome: St Peter’s and Vatican in foreground; Supreme Court large white building in right background by River Tiber]
It really ain’t over until it’s over, and knowing the hyper-cautious Italian justice system, maybe not even then.
Now the drama moves to Rome.
Before any verdict and sentence in the case can become final, under Italian law and the constitution the verdict and sentence must be endorsed by the Supreme Court of Cassation.
If either the prosecution or defenses demand that issues be looked at by Cassation (as we know, the prosecution will) Cassation will do so, and it may punt the case back down to the first appeal court to re-examine questions or even run a complete re-trial at first appeal level.
At Cassation level the prosecution is likely to have at least five advantages.
- 1) A confusing Hellman sentence report seems likely which won’t be able to dispose of the Massei and Micheli reports because the Hellman court did not re-examine all issues
2) Cassation’s ruling on the final appeal of Rudy Guede which points to three perps, and Cassation’s general tendency to side with trial courts against first-appeal courts.
3) The likelihood that only the prosecution will file issues for consideration by Cassation and not the defenses and so the prosecution will dominate all proceedings.
4) Amanda Knox and Raffaele Sollecito and entourages seem unlikely to be there in person for the Cassation hearings or a retrial, and emotive factors would be less in play.
5) The Italian media and Italian public opinion and increasingly UK and US opinion seem to be taking the position that the Hellman appeal decision was unsatisfactory.
Two days ago, the Sunday Times ran this fine analysis below by their reporter on the case, John Follain, of the open issues that will be facing Cassation and possibly again facing the lower appeal court.
With a dozen books out John Follain has by far the largest and most impressive book publishing record of any reporter on the case.
Publishers Hodder and Stoughton have announced that his book Death in Perugia: The Definitive Account of the Meredith Kercher Case will be released first in the UK later this month - on 25 October.
KILLER QUESTIONS; The acquittal last week of Amanda Knox only deepens the confusion surrounding the murder of the British student Meredith Kercher. John Follain, who has investigated the case for four years, unpicks the evidence How could one man pin Meredith down and inflict those injuries?
By John Follain in Perugia.
They may have been coached to hide their true feelings, but the expressions of the judges and jurors were an open book. Surprise and shock registered on the faces of the appeal tribunal in Perugia as they watched a video taken by the forensic police who searched the whitewashed cottage where Meredith Kercher was murdered.
That summer’s day in the medieval, vaulted Hall of Frescoes was the pivotal scene of the 10-month appeal trial of Amanda Knox, 24, and Raffaele Sollecito, 26 “” the moment that freedom suddenly became possible, if not probable, for the former lovers.
The rotund, bespectacled Stefano Conti, one of two specialists in forensic medicine appointed by the court to review two crucial traces of DNA evidence, gave a sardonic running commentary on the behaviour of the Roman scientific squad searching for clues in the cottage. They failed to use clean protective gloves to handle each item of evidence or biological sample, Conti pointed out. They passed Meredith’s bra clasp to one another before placing it back on the floor where they had found it. The officer who picked up her bra wore no gloves at all.
As the senior appeal judge, Claudio Pratillo Hellmann, recalled last week after acquitting Knox and Sollecito of sexually abusing and murdering Meredith, the DNA review was “the most difficult moment” of the trial.
“The prosecutors understood that their case was at risk, and it was at that moment that the trial became a battle with no holds barred,” he said.
The courtroom fight over this international cause célèbre ended with a sobbing Knox being rushed out by guards and flown home to a heroine’s welcome in Seattle.
But, far from resolving the mystery of how and why Meredith died, the acquittal has fuelled the unanswered questions over her fate. Are we “back to square one”, as Meredith’s brother Lyle said after the verdict? What are the mysteries still to be resolved? And will we ever know what truly happened? MEREDITH, a 21-year-old language student from Coulsdon, Surrey, was found lying virtually naked, her throat cut, in her bedroom in the house she shared with Knox and two other young women on the afternoon of November 2, 2007. “Case closed,” an overoptimistic police chief proclaimed just four days later.
The investigators thought Knox had handed them the keys to the mystery. Under questioning she placed herself at the crime scene on the night before the body was found. She had been in the kitchen, with her hands over her ears, she said, while Patrick Lumumba, a Congolese bar owner for whom she worked as a waitress, killed Meredith.
Police promptly arrested Lumumba, Knox and her boyfriend. But Knox later went back on her testimony, insisting she had been with Sollecito at his flat all night.
Investigators were forced to release Lumumba after witnesses testified he had been working at his bar on the night of the murder. Knox and Sollecito stayed behind bars.
Forensic evidence then prompted the arrest of another African immigrant, Rudy Guede, an Ivory Coast drifter. Part of his palm print was on a cushion under Meredith’s body, his DNA was in her body where he had apparently groped her sexually, and his DNA was mixed with hers in drops of blood inside her shoulder bag.
The prosecutor, Giuliano Mignini, accused Guede, Knox and Sollecito of killing Meredith when she resisted their attempts to force her into a sex game.
Certainly, there appeared to be compelling evidence that Knox was lying. She had tried to frame Lumumba. The defence now claimed that an intruder had broken into the cottage and attacked Meredith; but the break-in had clearly been staged. Amateurishly, a room had been ransacked before the window into it was smashed “” the glass lay over the strewn clothes instead of under them. Was this to cover Knox’s tracks? There were mixed traces of Knox’s and Meredith’s blood in the bathroom and another room. Bloody footprints had been left by Knox and Sollecito in the bathroom and in the corridor. Knox had behaved bizarrely at the police station after the murder, kissing and caressing Sollecito and doing yoga exercises. Sollecito had said he spent much of the murder night on his computer, but this was disproved by experts.
Still, this was all circumstantial evidence rather than proof. The Rome forensic police came to the rescue of the prosecution team. They reported that Meredith’s DNA was on the blade of a kitchen knife found at Sollecito’s flat “” and Knox’s was on the handle. This was believed to be one of the murder weapons.
Forensic pathologists said Meredith’s wounds had been caused by two knives, pointing to more than one killer. The team from Rome also reported that Sollecito’s DNA was on Meredith’s bra clasp. (Only much later would it emerge that the police had retrieved this from the bedroom floor a full 46 days after first spotting it.) The case rapidly became a sensation. The prime suspect was an intelligent and alluringly pretty American, only 20 at the time, who, reporters joyously discovered, had been nicknamed “Foxy Knoxy” back home in Seattle. That this was for her skills on the soccer pitch was lost in the rush to find out more.
Dozens of witnesses and expert consultants passed through Perugia’s Hall of Frescoes during the first trial, which lasted for much of 2009.
Knox was portrayed by the lawyer for the bar owner, Lumumba, as an unscrupulous and manipulative she-devil, and by her defence team as “a wholesome girl” wrongly accused.
The prosecution case was that Kercher, a hard-working young woman from a modest background, had become exasperated by Knox’s slovenly and promiscuous behaviour as a housemate.
She had remarked to her father that “Amanda arrived only a week ago and she already has a boyfriend”. She told friends that Knox left a vibrator and condoms in the bathroom and brought “strange men” to the cottage. Investigators leaked Knox’s diary, in which she had listed seven sexual partners, three of whom she had slept with after her arrival in Italy, including a man she had met on the train on her way to Perugia. On Facebook she had put down as her interests: “Men.” Unable to prove exactly what had happened on the night of the murder, Mignini offered a plausible scenario based on Meredith’s 43 knife wounds and bruises.
He suggested that an argument between Meredith and Knox escalated when Guede and Sollecito joined the American “under the influence of drugs and maybe of alcohol” in trying to force Kercher into a heavy sex game that ended in murder. The sensational 11-month trial ended in guilty verdicts and jail sentences of 26 years for Knox and 25 years for Sollecito.
Some months later, in August 2010, I met Knox briefly in Capanne women’s prison, which is a short drive from Perugia. She had cut her hair and looked younger and more frail than during her trial. She wore a red Beatles sweatshirt, black leggings and silver nail varnish.
When I arrived, she was pushing a trolley down a corridor.
A guard explained that her job was to collect orders from other prisoners for small goods they could buy: newspapers, cigarettes, coffee, magazines and “” at that time of year “” strawberries. We were allowed to talk for only a few moments, but a guard told me: “She’s pretty well. Amanda’s confident that the future will bring freedom for her. She doesn’t break down in tears. It’s nothing like the night of tears after the verdict, when we had to comfort her.”
I was told she had been reading “” in Italian “” the 427-page summary by the two judges at her trial, who had dissected the inconsistencies in her evidence.
This summary included the judges’ own reconstruction of what might have happened on the night of the murder, based on the evidence that had been put before them.
They suggested that Knox, Sollecito and Guede had arrived at the cottage at about 11pm. Knox and her boyfriend had gone to her bedroom to have sex, and, excited by a situation “heavy with sexual stimulus”, Guede had walked into Kercher’s room wanting to have sex with her.
Kercher rejected him “” she was tired, and had a new boyfriend anyway “” but Knox and Sollecito intervened to assist him. According to the judges, they were probably drugged on hashish and seeking “erotic sexual violence”. Forcing Kercher to yield to Guede was a “special thrill that had to be tried out”.
They suggested Sollecito cut Meredith’s bra with a small knife he always carried “” collecting knives was a hobby. As Guede sexually assaulted Kercher with his fingers, Sollecito stabbed her in the neck. Kercher screamed “” a neighbour heard her “” and Knox stabbed her in the throat with a kitchen knife, the judges argued. She took several minutes to die as she inhaled her own blood.
THAT was the lurid and damning case that Knox had to fight when she returned to the Hall of Frescoes last November for her appeal.
Her demeanour had changed. Gone was smiling and self-confident “Foxy”, whose manner may have helped secure her conviction. After three years in prison, Knox was much more demure.
The appeal hearing began auspiciously for her when the deputy judge remarked: “The only certain and undisputed fact is the death of Meredith Kercher.”
The comment prompted prosecutors to complain that the court had already made up its mind, but it was a portent of what was about to be revealed.
The appeal court’s decision to grant a defence request for an independent review of two items of DNA evidence “” the kitchen knife and the bra clasp “” proved devastating for the prosecution’s case.
The two experts “” Conti and Carla Vecchiotti, from La Sapienza University in Rome “” said the DNA trace on the knife blade could not be attributed to Meredith because it was too slight. They said Sollecito’s Y chromosome was on the bra clasp, but it could have been the result of contamination by police mishandling of the evidence. From then on, the prosecutors fought a losing battle to discredit Conti and Vecchiotti.
Outside the courtroom the Knox camp’s media offensive exploited the experts’ conclusions.
Knox’s family “” her mother, father, stepfather and friends “” had come well primed for battle. Homes had been remortgaged and funds raised.
With the help of a PR company in Seattle, they dominated prime-time shows on the leading American TV networks, dramatically influencing public opinion there “” so much so that the prosecutor Mignini thundered in court that he had never seen a convict hire a PR firm to prove her innocence.
Mignini himself was a key target. In what appeared to have been a turf battle with prosecutors in Florence, he had been given a suspended 16-month prison sentence for abuse of office after tapping the phones of police officers and journalists in a separate investigation into a serial killer. It was a reflection of the fragmented and politicised condition of the Italian justice system.
The prosecutors tried but failed to switch the focus away from the forensic evidence by introducing Guede, the third party to the murder. He had been prosecuted separately because he had opted for a “fast track” trial that offers a lighter sentence as an incentive. Jailed for 16 years for murder, he had appealed to the Supreme Court in Rome “” Italy’s highest court “” which confirmed his conviction, ruling that Guede had sexually abused and murdered Kercher with “unidentified accomplices”.
This was an insight into the mystifying processes of Italian law. How could justice be served by trying Guede separately? Why had he not been brought to give evidence at the first Knox trial? Why were his accomplices “unidentified” when Knox and Sollecito had been convicted of joining him in the murder? The answers lay in the fact that his supreme court appeal started just after Knox’s appeal began in Perugia “” and the two cases overlapped, a bizarre way of seeking out the truth.
Once Guede’s Supreme Court appeal had been dismissed he was summoned to the witness box in Perugia, where his contribution was damning yet so limited that it did not sway the judges and jury.
Rather than taking him through the events of the killing, Mignini read out a letter in which Guede had written of “the horrible murder of a ... wonderful girl by Raffaele Sollecito and Amanda Knox”. Challenged by one of Knox’s lawyers, Guede stood by the letter, saying: “It’s not as if there is my truth, and the truth of Tom, Dick and Harry. What there is is the truth of what I lived through that night, full stop.”
A lawyer for the Kerchers detailed the injuries Meredith suffered, arguing it would have been impossible for Guede to hold her down, sexually assault her, try to suffocate her, try to strangle her and wound her with more than one knife.
But it was too late. The appeal panel of judges and jurors had made up their minds. A juror confided after the “not guilty” verdicts had been delivered that the court had decided to acquit because of doubts over the forensic evidence, and because it saw no motive for the murder.
Pratillo Hellman explained: “To convict, the penal code says you have to be persuaded beyond every reasonable doubt. The smallest doubt is enough to not condemn.”
But he added enigmatically: “Maybe Knox and Sollecito know what happened that night, because our acquittal verdict stems from the truth which was established in the trial. But the real truth can be different. They may be responsible, but there isn’t the evidence… So, perhaps they too know what happened that night, but that’s not our conclusion.”
The judge’s comments earned him a new nickname, which investigators texted to each other delightedly: “Pontius Pratillo”, after Pontius Pilate, who washed his hands of responsibility for the execution of Jesus Christ.
The prosecution scored one potentially significant victory. The court found Knox guilty of slandering the former bar owner Lumumba by initially claiming he had killed Kercher. It sentenced her to three years in prison, but released her as she had spent almost four years behind bars.
“That’s absurd, absurd,” Mignini fumed. “Knox accused Lumumba to throw the police off her tracks. Why else would she accuse him?” IN PERUGIA, at least, the prosecution can count on overwhelming backing. After the verdict, a crowd several thousand strong massed outside the courts, amid jeers at defence lawyers and chants of “Assassini, assassini!” (murderers, murderers) and “Vergogna, vergogna!” (shame, shame). In bars across the picturesque city, and on the main cobbled street, Corso Vannucci, many dissected the case for days afterwards “” the consensus was that Knox and Sollecito were at the cottage when Meredith died, but no one agreed on what role they played.
For the Kercher family no outcome could have been more bewildering. As Knox flew home, Meredith’s mother Arline, her brother Lyle and her sister Stephanie spoke to me.
“It almost raises more questions than there are answers now,” Lyle said, “because the initial decision was that [the murder] wasn’t done by one person but by more than that. Two have been released, one remains in jail, so we’re now left questioning: who are these other people or person?” Did they believe that Knox and Sollecito were guilty? “In a way we have to believe what the police say because they are the ones compiling the evidence,” Arline replied. “We haven’t a clue. I think that’s what he was saying. It’s the police “” it’s their job.”
“It’s difficult for anybody to make a valid opinion on any case, not just this one, unless you’re a trained expert,” Lyle echoed. “There are forensics, detectives, psychological profilers and so on, who are trained to do this and read the information and draw the hypotheses from that, which of course no lay person really is. So if that’s the conclusion they come to, then we’re happy to stand by that.”
“We have to accept, don’t we, just like now we have to accept this,” Arline said.
“And that’s why it’s so disappointing, because we don’t know,” Stephanie added.
It is not over for the Kerchers.
Last week’s acquittal is far from the last word on the case. The judges have 90 days to draft a report explaining the reasons for the verdict. Then the prosecution and the defence will have a further 45 days to lodge a new and last appeal. Only rulings by the Supreme Court are considered definitive in Italian justice.
Guede’s lawyers said he would appeal for a new trial if the Supreme Court confirmed Knox’s acquittal “” on the grounds that it would contradict the Ivorian’s conviction for killing Meredith alongside unidentified accomplices. “So I’m supposed to be Meredith’s only assassin?” Guede is reported to have told a prison visitor. “I’m supposed to have struck that poor girl with a knife 40 times? I confessed my responsibilities and I accused those who were in the house with me.
“I’m in prison, and the others are free and happy at home. If it wasn’t them in the house that damned evening, who are the other accomplices supposed to be? The money made available to Amanda and the media strategy helped to free her.”
Many investigators and lawyers admit privately that the Italian judicial system may simply never come up with a full and convincing explanation of Meredith’s death.
Italian justice is agonisingly slow. Judges and lawyers attend several trials in the same week, with the result that the appeal trial saw 20 days of hearings over no fewer than 10 months. It is also full of safeguards for defendants, including long preliminary hearings enshrined in the post-war constitution to eradicate the caricature of justice delivered by the courts under Mussolini.
Many of the most notorious cases in Italy’s post-war history have yet to be resolved in court. Silvio Berlusconi, the billionaire prime minister, is embroiled in a string of corruption, fraud and sex offence investigations and trials, and claims that leftist prosecutors are plotting to oust him.
This week Berlusconi will push through parliament a bill banning publication of phone and other intercepts before a case reaches trial “” a measure that has become a priority for him, as investigators are expected to release within a few weeks dozens of intercepts of reportedly embarrassing conversations between Berlusconi and a convicted drug dealer.
In such a climate Italian justice itself is on trial. The truth of what happened to Meredith Kercher may emerge one day, but it’s no safe bet that it will do so in an Italian court of law.
Tuesday, December 01, 2009
Andrea Vogt Asks Some Useful Questions Concerning The Legal Process
Posted by Peter Quennell
Click here to read all of this well-researched report on the Seattle P-I website.
After presenting an overview of the system similar to those posted here by Nicki and Commisario Montalbano Andrea Vogt asks two experts on the system these questions.
Do jurors have to find Knox guilty beyond a reasonable doubt?
Yes. The concept of proof beyond a reasonable doubt has long been a part of Italy’s justice system. It was formalized and passed into law in 2006.
Knox’s defense lawyer Luciano Ghirga said his team will remind jurors that, even after more than 40 hearings, everything is still in doubt.
The court’s ruling (which is not called a verdict in Italy) is made by an eight-member jury: six laymen and two professional judges. They will vote, and the majority rules. In the case of a 4-4 tie, acquittal overrules.
Could Amanda Knox have plea bargained?
Knox maintains her innocence.
However, while not completely analogous to plea bargaining, Italy does have a similar alternative to trial, also a part of the 1988 reforms. The alternative is not applicable for serious crimes, such as murder, punishable by more than five years in prison.
Suspects who cooperate fully with the police, however, may become eligible for a bundle of mitigating circumstances that would lower prison sentences. A judge may also choose to apply aggravating circumstances to increase a sentence.
Negotiation on the evidence—in which both sides agree what can be admitted—is also available when defendants choose a fast-track trial, as did Rudy Guede, sentenced to 30 years last year for his role in the case for which Knox is on trial. Guede is appealing his conviction.
Why does the figure of prosecutor seem so powerful in Italy?
The prosecutor is a powerful figure in Italy connected to the judiciary, not elected or appointed. While there is a career separation between judges and prosecutors, the qualifying examination and training are common, That has made judges and prosecutors close both culturally and professionally.
In the U.S., prosecutors are appointed in federal system and typically elected in the state system, hence it is common to hear cases referred to as The State vs. X.
In Italy, protections were put in place precisely to prevent the state from pursuing or persecuting, hence the independence of prosecutors.
As a result, prosecutors haven’t shied away from taking on politicians. Italian Premier Silvio Berlusconi, for example, faces a series of criminal procedures in the courts.
That independence , some argue, is precisely the protection needed as a check against government power, and without it, corruption could not be exposed, said Maffei. But others argue that prosecutors wage their own political battles. using their independence to attack political opponents.
Another major difference: the prosecutor supervises the investigation rather than letting police handle it.
Further, he or she also has no discretion over the decision to seek charges. There is a constitutional principle of mandatory prosecution. If there is sufficient evidence to build a case against a defendant, a prosecutor must seek an indictment.
In the U.S. prosecutors can and do drop cases for such reasons as workload or because the defendant has agreed to help with a criminal investigation.
Was it legal for Knox not to have an attorney present when police questioned her?
Yes and No.
Amanda Knox’s interrogation falls into a gray area of the law because she came voluntarily to the police station and was being interviewed in the beginning as someone who could become be a witness, not a suspect.
Then, in the course of questioning by police in November 2007, she blamed Patrick Lumumba for the slaying, and said she was present at the scene of the crime. Lumumba was innocent. Knox has since denied she knows anything about the slaying and says she wasn’t in the flat the night Kercher was killed. Limumba is suing Knox for slander.
The law is very clear: A suspect must not be interrogated without a lawyer.
Once a suspect, an interrogation must be interrupted, the suspect read his or her rights to remain silent and be provided a lawyer. Italian law does not allow waiver of one’s right to counsel. Even if a suspect doesn’t want a lawyer, the authorities are required to appoint one.
If a suspect’s freedom of movement is hindered, the interrogation must be videotaped.
In Knox’s case, a video or audio recording of the entire police interrogation (authorities have denied that any such recordings exist) could identify when police began treating Knox as a suspect and what procedures were followed.
In fact, Italy’s Supreme Court has already said that some of her early statements may not be used against her because they were made without an attorney present.


